RTMP è un protocollo di messaggistica in tempo reale sviluppato da Macromedia che può essere utilizzato per lo streaming di audio, video e dati su Internet. Nginx RTMP è uno streamer multimediale basato su Nginx che include molte funzionalità tra cui il supporto H264/AAC, la transcodifica online con FFmpeg, il supporto per la richiamata HTTP e un modulo di controllo HTTP per la registrazione di audio/video.
In questo tutorial, ti mostreremo come compilare Nginx con il modulo RTMP e creare un live streaming RTMP su CentOS 8.
Prerequisiti
- Un nuovo CentOS 8 VPS sulla piattaforma Atlantic.Net Cloud
- Una password di root configurata sul tuo server
Fase 1:crea un server cloud Atlantic.Net
Per prima cosa, accedi al tuo server Atlantic.Net Cloud. Crea un nuovo server, scegliendo CentOS 8 come sistema operativo con almeno 2 GB di RAM. Collegati al tuo Cloud Server tramite SSH e accedi utilizzando le credenziali evidenziate in alto nella pagina.
Dopo aver effettuato l'accesso al server CentOS 8, esegui il comando seguente per aggiornare il sistema di base con gli ultimi pacchetti disponibili.
yum update -y
Passaggio 2:installazione delle dipendenze richieste
Prima di iniziare, dovrai installare le dipendenze necessarie per compilare Nginx con supporto RTMP. Innanzitutto, installa il pacchetto del gruppo Strumento di sviluppo con il seguente comando:
yum groupinstall 'Development Tools' -y
Quindi, installa il repository EPEL con il seguente comando:
yum install epel-release -y
Una volta installato, installa le altre dipendenze richieste utilizzando il comando seguente:
yum install wget git unzip perl perl-devel perl-ExtUtils-Embed libxslt libxslt-devel libxml2 libxml2-devel gd gd-devel pcre-devel GeoIP GeoIP-devel -y
Una volta installati tutti i pacchetti, puoi procedere alla compilazione di Nginx.
Fase 3:scarica i componenti richiesti
Innanzitutto, dovrai scaricare i componenti necessari per compilare Nginx con il supporto RTMP.
Innanzitutto, scarica l'ultima versione stabile di Nginx con il seguente comando:
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
Una volta scaricato, estrailo utilizzando il seguente comando:
tar -xvzf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
Quindi, scarica PCRE e Zlib con il seguente comando:
wget https://ftp.pcre.org/pub/pcre/pcre-8.42.zip wget https://www.zlib.net/zlib-1.2.11.tar.gz
Una volta scaricati, estraili con il seguente comando:
unzip pcre-8.42.zip tar -xvzf zlib-1.2.11.tar.gz
Una volta estratti entrambi, scarica OpenSSL con il seguente comando:
wget https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.1.0h.tar.gz
Quindi, estrai il pacchetto scaricato con il seguente comando:
tar -xzvf openssl-1.1.0h.tar.gz
Quindi, scarica l'ultima versione del modulo Nginx RTMP dal repository Git utilizzando il seguente comando:
git clone https://github.com/sergey-dryabzhinsky/nginx-rtmp-module.git
Una volta scaricati tutti i componenti, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Fase 4:installa Nginx con supporto RTMP
Innanzitutto, cambia la directory in Nginx con il seguente comando:
cd nginx-1.18.0/
Quindi, configura Nginx con il supporto RTMP usando il comando seguente:
./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx \ --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx \ --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules \ --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \ --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \ --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid \ --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock \ --user=nginx \ --group=nginx \ --build=CentOS \ --builddir=nginx-1.18.0 \ --with-select_module \ --with-poll_module \ --with-threads \ --with-file-aio \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_v2_module \ --with-http_realip_module \ --with-http_addition_module \ --with-http_xslt_module=dynamic \ --with-http_image_filter_module=dynamic \ --with-http_geoip_module=dynamic \ --with-http_sub_module \ --with-http_dav_module \ --with-http_flv_module \ --with-http_mp4_module \ --with-http_gunzip_module \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --with-http_auth_request_module \ --with-http_random_index_module \ --with-http_secure_link_module \ --with-http_degradation_module \ --with-http_slice_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \ --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp \ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp \ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp \ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp \ --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp \ --with-mail=dynamic \ --with-mail_ssl_module \ --with-stream=dynamic \ --with-stream_ssl_module \ --with-stream_realip_module \ --with-stream_geoip_module=dynamic \ --with-stream_ssl_preread_module \ --with-compat \ --with-pcre=../pcre-8.42 \ --with-pcre-jit \ --with-zlib=../zlib-1.2.11 \ --with-openssl=../openssl-1.1.0h \ --with-openssl-opt=no-nextprotoneg \ --add-module=../nginx-rtmp-module \ --with-debug
Una volta completato il processo di configurazione, dovresti ottenere il seguente output:
Configuration summary + using threads + using PCRE library: ../pcre-8.42 + using OpenSSL library: ../openssl-1.1.0h + using zlib library: ../zlib-1.2.11 nginx path prefix: "/etc/nginx" nginx binary file: "/usr/sbin/nginx" nginx modules path: "/usr/lib64/nginx/modules" nginx configuration prefix: "/etc/nginx" nginx configuration file: "/etc/nginx/nginx.conf" nginx pid file: "/var/run/nginx.pid" nginx error log file: "/var/log/nginx/error.log" nginx http access log file: "/var/log/nginx/access.log" nginx http client request body temporary files: "/var/cache/nginx/client_temp" nginx http proxy temporary files: "/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp" nginx http fastcgi temporary files: "/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp" nginx http uwsgi temporary files: "/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp" nginx http scgi temporary files: "/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp"
Quindi, installa Nginx con il seguente comando:
make make install
Dopo aver installato Nginx, verifica la versione installata di Nginx con il seguente comando:
nginx -V
Dovresti ottenere il seguente output:
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0 (CentOS) built by gcc 8.3.1 20191121 (Red Hat 8.3.1-5) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.1.0h 27 Mar 2018 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules- path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log- path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock -- user=nginx --group=nginx --build=CentOS --builddir=nginx-1.14.0 --with-select_module --with- poll_module --with-threads --with-file-aio --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with- http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_xslt_module=dynamic --with- http_image_filter_module=dynamic --with-http_geoip_module=dynamic --with-http_sub_module -- with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with- http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with- http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module -- with-http_slice_module --with-http_stub_status_module --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log - -http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp- path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http- uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --with-mail=dynamic --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream=dynamic --with-stream_ssl_module -- with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_geoip_module=dynamic --with- stream_ssl_preread_module --with-compat --with-pcre=../pcre-8.42 --with-pcre-jit --with- zlib=../zlib-1.2.11 --with-openssl=../openssl-1.1.0h --with-openssl-opt=no-nextprotoneg --add- module=../nginx-rtmp-module --with-debug
Passaggio 5:crea un file di servizio Systemd per Nginx
Successivamente, dovrai creare un file di servizio Nginx per gestire il servizio Nginx. Puoi crearlo con il seguente comando:
nano /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
Aggiungi le seguenti righe:
[Unit] Description=nginx - high performance web server Documentation=https://nginx.org/en/docs/ After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/var/run/nginx.pid ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Salva e chiudi il file quando hai finito, quindi ricarica il demone systemd con il seguente comando:
systemctl daemon-reload
Quindi, avvia Nginx e abilitalo all'avvio al riavvio del sistema con il seguente comando:
systemctl start nginx systemctl enable nginx
Passaggio 6:configurare Nginx per utilizzare RTMP
First, create a backup copy of the Nginx main configuration file with the following command: mv /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.bak
Quindi, crea un nuovo file di configurazione Nginx usando il seguente comando:
nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Aggiungi le seguenti righe:
worker_processes auto;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
# RTMP configuration
rtmp {
server {
listen 1935; # Listen on standard RTMP port
chunk_size 4000;
# Define the Application
application show {
live on;
# Turn on HLS
hls on;
hls_path /mnt/hls/;
hls_fragment 3;
hls_playlist_length 60;
# disable consuming the stream from nginx as rtmp
deny play all;
}
}
}
http {
sendfile off;
tcp_nopush on;
aio on;
directio 512;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server {
listen 8080;
location / {
# Disable cache
add_header 'Cache-Control' 'no-cache';
# CORS setup
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*' always;
add_header 'Access-Control-Expose-Headers' 'Content-Length';
# allow CORS preflight requests
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*';
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 204;
}
types {
application/dash+xml mpd;
application/vnd.apple.mpegurl m3u8;
video/mp2t ts;
}
root /mnt/;
}
}
} Salva e chiudi il file, quindi crea una nuova directory per la configurazione HLS e assegna la proprietà adeguata:
mkdir -p /mnt/hls chown -R nginx:nginx /mnt/hls
Salva e chiudi il file quando hai finito.
Passaggio 7:crea streaming live RTMP
Successivamente, dovrai creare un video in streaming RTMP e creare un nuovo streaming RTMP live. Puoi farlo modificando il file di configurazione principale di Nginx:
nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Trova le seguenti righe:
hls_playlist_length 60; # disable consuming the stream from nginx as rtmp deny play all; }
Aggiungi le seguenti righe esattamente sotto la riga sopra:
application vod {
play /mnt/mp4s;
}
# RTMP stream using OBS
application stream {
live on;
} Salva e chiudi il file, quindi riavvia il servizio Nginx con il seguente comando:
systemctl restart nginx
Quindi, crea una directory in cui archiviare video MP4:
mkdir -p /mnt/mp4s
Quindi, scarica il video di esempio utilizzando il seguente comando:
cd /mnt/mp4s wget https://file-examples-com.github.io/uploads/2017/04/file_example_MP4_480_1_5MG.mp4 -O myfile.mp4
Quindi, dai la proprietà adeguata alla directory /mnt/mp4s:
chown -R nginx:nginx /mnt/mp4s
Passaggio 8:installa FFmpeg e avvia il server di streaming
Innanzitutto, dovrai installare FFmpeg nel tuo server. Per impostazione predefinita, non è installato nel repository predefinito di CentOS 8, quindi dovrai abilitare il repository Powertool nel tuo sistema. Puoi abilitarlo con il seguente comando:
yum install epel-release dnf-utils yum-config-manager --set-enabled PowerTools yum-config-manager --add-repo=https://negativo17.org/repos/epel-multimedia.repo
Quindi, installa FFmpeg con il seguente comando:
yum install ffmpeg -y
Una volta installato FFmpeg, avvia il server di streaming con il seguente comando:
ffmpeg -re -i /mnt/mp4s/myfile.mp4 -vcodec libx264 -vprofile baseline -g 30 -acodec aac -strict -2 - f flv rtmp://your-server-ip:1935/show/vod
Passaggio 9:prova lo streaming RTMP
Successivamente, dovrai testare lo stream vod RTMP con VLC media player.
Una volta che il sistema client, apri il lettore multimediale VLS, vai su VLC Media => Apri flusso di rete . Dovresti vedere la seguente schermata:
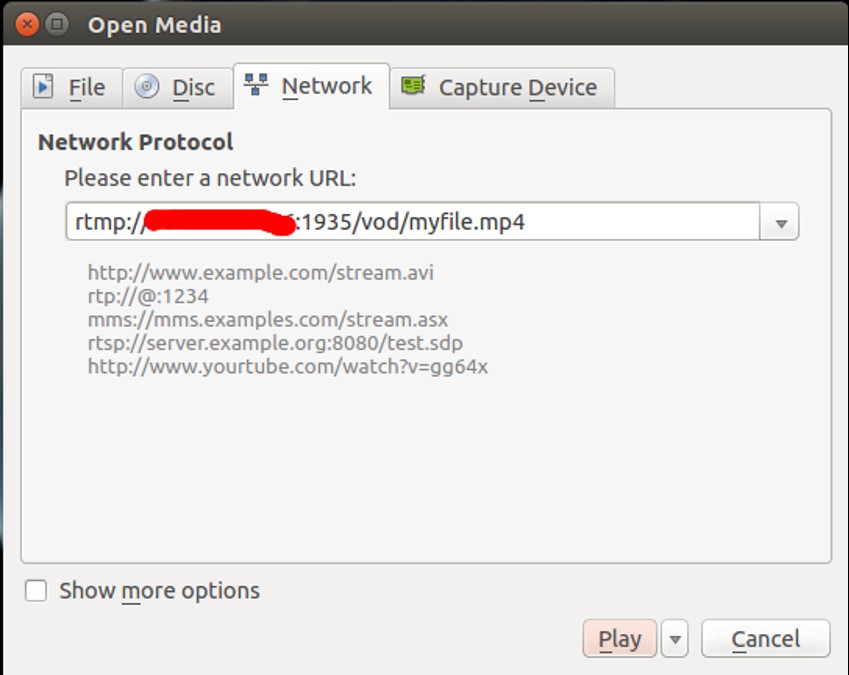
Fornisci l'URL del tuo server di streaming RTMP e fai clic su Riproduci pulsante.
Una volta connesso correttamente, dovresti vedere il tuo video MP4 nella seguente schermata:
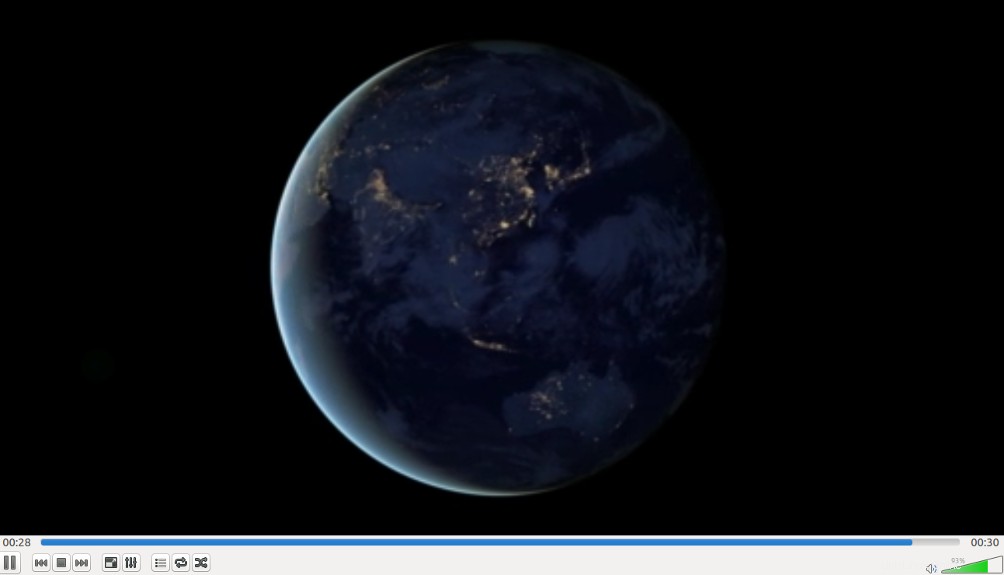

Conclusione
Nel tutorial sopra, hai imparato come installare Nginx con il supporto RTMP. Hai anche imparato come configurare Nginx per lo streaming di video MP4 e riprodurlo con VLC media player dal sistema remoto. Prova a installare Nginx con supporto RTMP su VPS Hosting da Atlantic.Net oggi!
Scopri di più sui nostri servizi di hosting VPS e sui server privati virtuali.