WordPress è un CMS gratuito, open source e il più popolare al mondo costruito interamente in PHP. Viene utilizzato da migliaia di persone in tutto il mondo per la gestione di blog, siti Web aziendali e negozi di e-commerce. Ha alcune fantastiche funzionalità tra cui un pannello di amministrazione semplice e facile da usare, migliaia di plug-in, una vasta comunità, temi approfonditi, personalizzazione e altro ancora.
In questa guida ti mostreremo come installare WordPress con Apache e Let's Encrypt SSL su AlmaLinux 8.
Prerequisiti
- Un server che esegue AlmaLinux 8.
- Un nome di dominio valido puntato all'IP del tuo server.
- Sul server è configurata una password di root.
Installa il server LAMP
WordPress richiede che il server LAMP sia installato nel tuo server. Puoi installarlo usando il seguente comando:
dnf install httpd mariadb-server php php-mysqlnd php-dom php-simplexml php-xml php-xmlreader php-curl php-exif php-ftp php-gd php-iconv php-json php-mbstring php-posix php-sockets php-tokenizer unzip -y
Dopo aver installato il server LAMP, avvia il servizio Apache e MariaDB e abilita l'avvio al riavvio del sistema:
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable mariadb
systemctl enable httpd
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Configura il database MariaDB
Innanzitutto, dovrai impostare la password di root di MariaDB e proteggere l'installazione di MariaDB. Puoi farlo usando il seguente comando:
mysql_secure_installation
Rispondi a tutte le domande come mostrato di seguito:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Set root password? [Y/n] Y New password: Re-enter new password: Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
Al termine, accedi a MariaDB con il seguente comando:
mysql -u root -p
Una volta effettuato l'accesso, crea un database e un utente per WordPress:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE wordpress;
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER `wordpress`@`localhost` IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Quindi, concedi tutti i privilegi al database di WordPress usando il comando seguente:
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON wordpress.* TO `wordpress`@`localhost`;
Quindi, svuota i privilegi ed esci dalla shell MariaDB con il seguente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> EXIT;
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Scarica WordPress
Quindi, cambia la directory nella radice web di Apache e scarica l'ultima versione di WordPress usando il seguente comando:
cd /var/www/html
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
Una volta completato il download, estrai il file scaricato con il seguente comando:
tar -xvzf latest.tar.gz
Quindi, cambia la directory in wordpress e rinomina il file di configurazione di esempio:
cd wordpress
mv wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php
Successivamente, modifica il file di configurazione con il seguente comando:
nano wp-config.php
Definisci la configurazione del tuo database come mostrato di seguito:
/** The name of the database for WordPress */ define( 'DB_NAME', 'wordpress' ); /** MySQL database username */ define( 'DB_USER', 'wordpress' ); /** MySQL database password */ define( 'DB_PASSWORD', 'password' ); /** MySQL hostname */ define( 'DB_HOST', 'localhost' );
Salva e chiudi il file quando hai finito, quindi imposta i permessi appropriati per la directory di WordPress:
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/wordpress
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Configura Apache per WordPress
Successivamente, dovrai creare un file di configurazione dell'host virtuale Apache per WordPress. Puoi crearlo con il seguente comando:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/wordpress.conf
Aggiungi le seguenti righe:
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/wordpress" ServerName wordpress.example.com ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/example.com-error_log" CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/example.com-access_log" combined <Directory "/var/www/html/wordpress"> DirectoryIndex index.html index.php Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> </VirtualHost>
Salva e chiudi il file, quindi riavvia il servizio Apache per applicare le modifiche:
systemctl restart httpd
Puoi controllare lo stato dell'Apache con il seguente comando:
systemctl status httpd
Dovresti ottenere il seguente output:
? httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2021-07-09 03:30:47 EDT; 3s ago
Docs: man:httpd.service(8)
Main PID: 4153 (httpd)
Status: "Started, listening on: port 80"
Tasks: 213 (limit: 12524)
Memory: 24.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
??4153 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
??4155 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
??4156 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
??4157 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
??4158 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
Jul 09 03:30:47 AlmaLinux systemd[1]: Stopped The Apache HTTP Server.
Jul 09 03:30:47 AlmaLinux systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Proteggi WordPress con Let's Encrypt SSL
Successivamente, dovrai installare il client Certbot per installare Let's Encrypt SSL per WordPress. Puoi installarlo con il seguente comando:
dnf install epel-release -y
dnf install certbot python3-certbot-apache
Quindi, ottieni e installa un certificato SSL per il tuo dominio Lets con il seguente comando:
certbot --apache -d wordpress.example.com
Ti verrà chiesto di fornire il tuo indirizzo email e di accettare i termini del servizio:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server. Do you agree? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing, once your first certificate is successfully issued, to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Account registered. Requesting a certificate for wordpress.example.com Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for wordpress.example.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/httpd/conf.d/wordpress.conf Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/httpd/conf.d/wordpress.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://wordpress.example.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Subscribe to the EFF mailing list (email: [email protected]). IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/wordpress.example.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/wordpress.example.com/privkey.pem Your certificate will expire on 2022-02-09. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Configura Firewall
Successivamente, dovrai consentire le porte 80 e 443 attraverso il firewalld. Puoi consentirli con il seguente comando:
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
Quindi, ricarica il firewalld per applicare le modifiche:
firewall-cmd --reload
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Accedi al dashboard di WordPress
Quindi, apri il tuo browser web e accedi al pannello di amministrazione di WordPress utilizzando l'URL https://wordpress.example.com . Verrai reindirizzato alla seguente pagina:
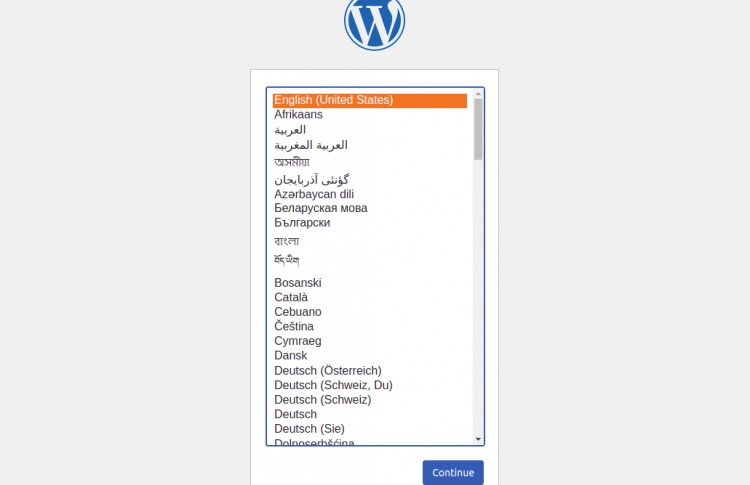
Seleziona la tua lingua e fai clic su Continua . Dovresti vedere la pagina di configurazione del sito WordPress:
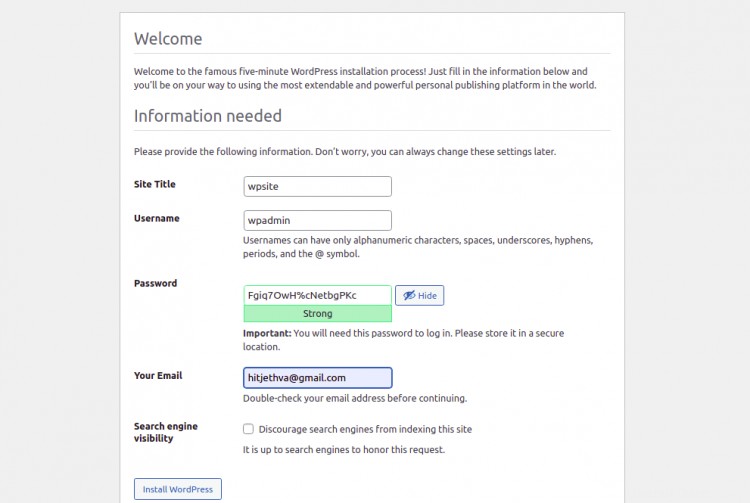
Fornisci le informazioni sul tuo sito e fai clic su Installa WordPress pulsante. Una volta completata l'installazione, dovresti vedere la seguente pagina:

Fai clic su Accedi pulsante. Verrai reindirizzato alla pagina di accesso di WordPress:

Fornisci il nome utente e la password dell'amministratore e fai clic su Accedi pulsante. Dovresti vedere la dashboard di WordPress nella pagina seguente:
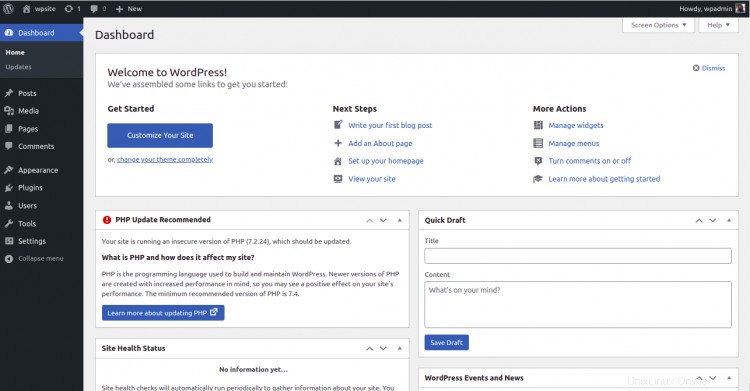
Conclusione
Congratulazioni! hai installato con successo WordPress con Apache e Let's Encrypt SSL su AlmaLinux 8. Ora puoi creare facilmente il tuo sito web usando WordPress. Sentiti libero di chiedermi se hai domande.