Gitea è un sistema di controllo della versione open source e self-hosted scritto in Go. È semplice, leggero e può essere installato su sistemi a bassa potenza. È un fork di Gogs e un'alternativa a GitHub e GitLab. Viene fornito con molte funzionalità tra cui editor di file di repository, monitoraggio dei problemi del progetto, gestione degli utenti, notifiche, wiki integrato e molto altro. Può essere installato su tutti i moderni sistemi operativi, incluse le architetture Linux, macOS, Windows, ARM e PowerPC.
In questo tutorial, ti mostreremo come installare il servizio Gitea Git con Nginx e Let's Encrypt SSL su Ubuntu 20.04.
Prerequisiti
- Un server che esegue Ubuntu 20.04.
- Un nome di dominio valido punta al tuo server.
- Sul tuo server è configurata una password di root.
Installa Git
Innanzitutto, dovrai installare il pacchetto Git nel tuo server. Puoi installarlo eseguendo il seguente comando:
apt-get install git -y
Una volta installato il pacchetto Git, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Installa e configura MariaDB
Per impostazione predefinita, MariaDB non è protetta. Quindi, dovrai prima proteggerlo. Puoi proteggerlo eseguendo lo script mysql_secure_installation:
mysql_secure_installation
Questo script imposterà la password di root, rimuoverà gli utenti anonimi, non consentirà l'accesso root in remoto e rimuoverà il database di test come mostrato di seguito:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Set root password? [Y/n]: Y Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]: Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]: Y
Una volta che MariaDB è protetto, accedi alla shell di MariaDB con il seguente comando:
mysql -u root -p
Inserisci la tua password di root quando richiesto. Quindi, cambia GLOBAL innodeb_file_per_table su On:
MariaDB [(none)]>SET GLOBAL innodb_file_per_table = ON;
Quindi, crea un database e un utente per Gitea con il seguente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]>CREATE DATABASE giteadb;
MariaDB [(none)]>CREATE USER 'gitea'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Quindi, concedi tutti i privilegi al database giteadb:
MariaDB [(none)]>GRANT ALL ON giteadb.* TO 'gitea'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Quindi, aggiorna il set di caratteri del database con il seguente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]>ALTER DATABASE giteadb CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
Infine, svuota i privilegi ed esci dalla shell MariaDB con il seguente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]>FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]>EXIT;
Successivamente, dovrai modificare il file di configurazione predefinito di MariaDB e aggiungere i parametri innodb:
nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Aggiungi le seguenti righe all'interno della sezione [mysqld]:
innodb_file_format = Barracuda innodb_large_prefix = 1 innodb_default_row_format = dynamic
Salva e chiudi il file. Quindi, riavvia il servizio MariaDB per applicare le modifiche:
systemctl restart mariadb
A questo punto, il tuo database MariaDB è configurato. Ora puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Installa e configura Gitea
Innanzitutto, dovrai scaricare l'ultima versione del binario Gitea dal repository Git. Puoi scaricarlo con il seguente comando:
wget https://dl.gitea.io/gitea/1.12.1/gitea-1.12.1-linux-amd64
Quindi, copia il file scaricato nella directory /usr/bin/ e dai i permessi di esecuzione:
cp gitea-1.12.1-linux-amd64 /usr/bin/gitea
chmod 755 /usr/bin/gitea
Quindi, crea un utente di sistema per Gitea con il seguente comando:
adduser --system --shell /bin/bash --group --disabled-password --home /home/git git
Quindi, crea una struttura di directory per Gitea con il seguente comando:
mkdir -p /etc/gitea /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
chown git:git /etc/gitea /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chmod 770 /etc/gitea Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Crea file di servizio Gitea Systemd
Successivamente, dovrai creare un file di servizio systemd per gestire il servizio Gitea. Puoi crearlo con il seguente comando:
nano /etc/systemd/system/gitea.service
Aggiungi le seguenti righe:
[Unit] Description=Gitea After=syslog.target After=network.target After=mysql.service [Service] RestartSec=2s Type=simple User=git Group=git WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/gitea/ ExecStart=/usr/bin/gitea web -c /etc/gitea/app.ini Restart=always Environment=USER=git HOME=/home/git GITEA_WORK_DIR=/var/lib/gitea [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Salva e chiudi il file. Quindi, ricarica il demone systemd e avvia il servizio Gitea con il seguente comando:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start gitea
Ora puoi controllare lo stato del servizio Gitea con il seguente comando:
systemctl status gitea
Dovresti vedere il seguente output:
? gitea.service - Gitea
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/gitea.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2020-06-25 08:23:01 UTC; 6s ago
Main PID: 24046 (gitea)
Tasks: 9 (limit: 2353)
Memory: 134.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/gitea.service
??24046 /usr/bin/gitea web -c /etc/gitea/app.ini
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 routers/init.go:127:GlobalInit() [I] Delete all repository archives
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 ...dules/setting/log.go:233:newLogService() [I] Gitea v1.12.1 built with GNU Make 4>
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 ...dules/setting/log.go:279:newLogService() [I] Gitea Log Mode: Console(Console:inf>
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 ...les/setting/cache.go:70:newCacheService() [I] Cache Service Enabled
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 ...les/setting/cache.go:81:newCacheService() [I] Last Commit Cache Service Enabled
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 ...s/setting/session.go:63:newSessionService() [I] Session Service Enabled
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 routers/init.go:165:GlobalInit() [I] SQLite3 Supported
Jun 25 08:23:02 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:02 routers/init.go:51:checkRunMode() [I] Run Mode: Development
Jun 25 08:23:03 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:03 cmd/web.go:161:runWeb() [I] Listen: http://0.0.0.0:3000
Jun 25 08:23:03 ubuntu20 gitea[24046]: 2020/06/25 08:23:03 ...s/graceful/server.go:55:NewServer() [I] Starting new server: tcp:0.0.0.0:3000 on>
lines 1-19/19 (END)
Successivamente, abilita l'avvio del servizio Gitea al riavvio del sistema con il seguente comando:
systemctl enable gitea
A questo punto Gitea è avviato ed è in ascolto sulla porta 3000. Ora puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Configura Nginx per Gitea
Per impostazione predefinita, Gitea è in ascolto sulla porta 3000. Quindi, dovrai configurare Nginx come proxy inverso per accedere a Gitea senza specificare la porta.
Innanzitutto, installa il server web Nginx eseguendo il seguente comando:
apt-get install nginx -y
Una volta installato, crea un nuovo file di configurazione dell'host virtuale Nginx per Gitea:
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/gitea
Aggiungi le seguenti righe:
upstream gitea {
server 127.0.0.1:3000;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name gitea.linuxbuz.com;
root /var/lib/gitea/public;
access_log off;
error_log off;
location / {
try_files maintain.html $uri $uri/index.html @node;
}
location @node {
client_max_body_size 0;
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 0;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_read_timeout 120;
}
}
Salva e chiudi il file. Quindi, abilita il file di configurazione dell'host virtuale Nginx con il seguente comando:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/gitea /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Infine, riavvia il servizio Nginx con il seguente comando:
systemctl restart nginx
Puoi anche controllare lo stato del servizio Nginx con il seguente comando:
systemctl status nginx
Dovresti ottenere il seguente output:
? nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2020-06-25 08:26:00 UTC; 1min 24s ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Process: 24866 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 24877 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 24879 (nginx)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 2353)
Memory: 3.6M
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??24879 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;
??24880 nginx: worker process
??24881 nginx: worker process
Jun 25 08:25:59 ubuntu20 systemd[1]: Starting A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server...
Jun 25 08:26:00 ubuntu20 systemd[1]: Started A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server.
A questo punto, Nginx è configurato per servire Gitea. Ora puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Proteggi Gitea con Let's Encrypt SSL
Innanzitutto, dovrai installare il client Certbot per installare e gestire Let's Encrypt SSL nel tuo sistema. Puoi installarlo eseguendo il seguente comando:
apt-get install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
Una volta installato Certbot, eseguire il comando seguente per scaricare e installare il sito Web Let's Encrypt SSL per Gitea.
certbot --nginx -d gitea.linuxbuz.com
Fornisci il tuo indirizzo email e accetta i termini del servizio come mostrato di seguito:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for gitea.linuxbuz.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/gitea
Quindi, scegli se reindirizzare o meno il traffico HTTP su HTTPS come mostrato di seguito:
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Digita 2 e premi Invio per installare il certificato come mostrato di seguito:
Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/gitea - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://gitea.linuxbuz.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=gitea.linuxbuz.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/gitea.linuxbuz.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/gitea.linuxbuz.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2020-09-23. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Ora, il tuo sito web Gitea è protetto con Let's Encrypt SSL. Ora puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Accedi all'interfaccia web di Gitea
Ora apri il tuo browser web e digita l'URL https://gitea.linuxbuz.com/install. Verrai reindirizzato alla seguente pagina:
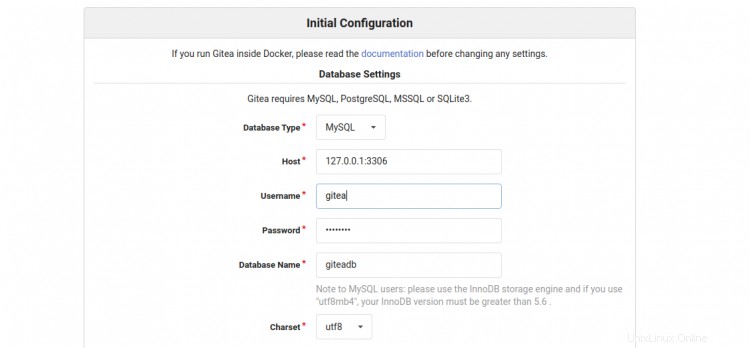
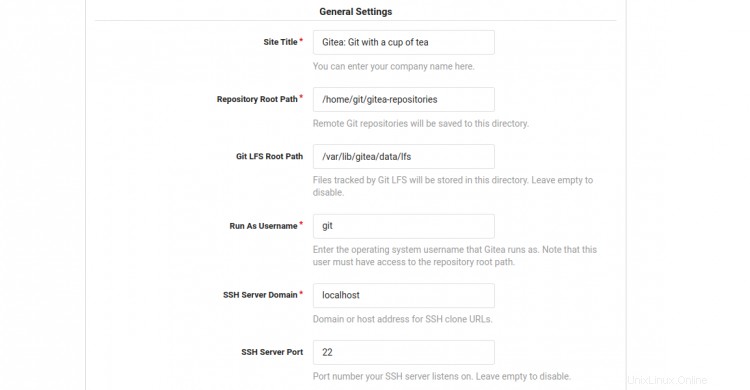
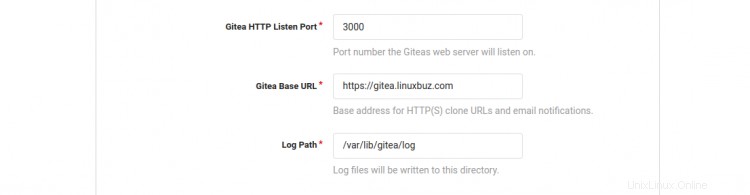
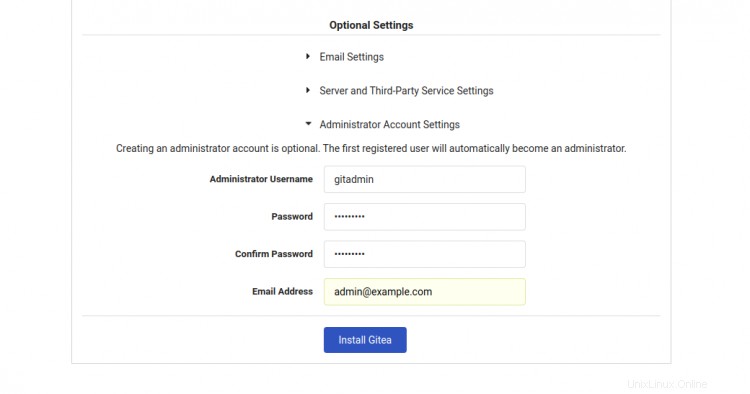
Fornisci il nome del tuo database Gitea, nome utente, password, percorso del repository, esegui come nome utente, porta di ascolto, URL di base Gitea, percorso di registro, nome utente amministratore Gitea, password e fai clic su Installa Gitea pulsante. Una volta terminata l'installazione, dovresti vedere la dashboard di Gitea nella seguente schermata:
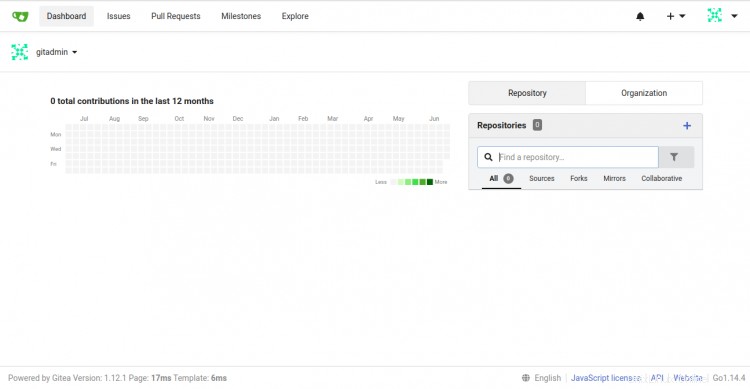
Conclusione
Congratulazioni! hai installato con successo Gitea con Nginx e Let's Encrypt SSL sul server Ubuntu 20.04. Ora puoi esplorare Gitea e creare il tuo primo repository con Gitea. Per ulteriori informazioni, visita la documentazione Gitea.