MariaDB è uno dei più popolari sistemi di gestione di database open source utilizzati dalle piccole e grandi imprese. È un fork del famoso server di database MySQL, sviluppato da MariaDB Corporation Ab, guidato dagli sviluppatori originali di MySQL.
MariaDB è completamente compatibile con MySQL per garantire una capacità di sostituzione drop-in. MariaDB viene spesso utilizzato come server di database nello stack LAMP e LEMP.
LEGGI: Come installare lo stack LAMP su CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
LEGGI: Come installare lo stack LEMP su CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
In questo post vedremo come installare MariaDB su CentOS 8 / RHEL 8.
Installa MariaDB su CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
Puoi ottenere i pacchetti MariaDB per CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 in due modi.
- Repository Red Hat (v10.3)
- Mirror ufficiale MariaDB (v10.4)
Installa MariaDB dal repository AppStream
L'installazione di MariaDB dal repository AppStream è semplice. Ma il repository potrebbe avere una versione un po' vecchia del pacchetto MariaDB.
yum -y install @mariadb
Installa MariaDB dal mirror ufficiale di MariaDB
La fondazione MariaDB offre pacchetti MariaDB per CentOS 8 / RHEL 8. I pacchetti forniti da MariaDB sono sempre aggiornati e supportati dalla comunità di MariaDB.
CentOS 8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/centos8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
RHEL 8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/rhel8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
Installa il server MariaDB usando il seguente comando.
È necessario disabilitare temporaneamente il repository rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms e AppStream su RHEL 8 e CentOS 8 per consentire a yum di scaricare i pacchetti dal mirror MariaDB.### CentOS 8 ### yum install -y boost-program-options yum --disablerepo=AppStream install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client ### RHEL 8 ### yum --disablerepo=rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
Gestisci il servizio MariaDB
Nel caso in cui desideri avviare/arrestare il servizio MariaDB, puoi utilizzare i seguenti comandi.
systemctl start mariadb systemctl stop mariadb
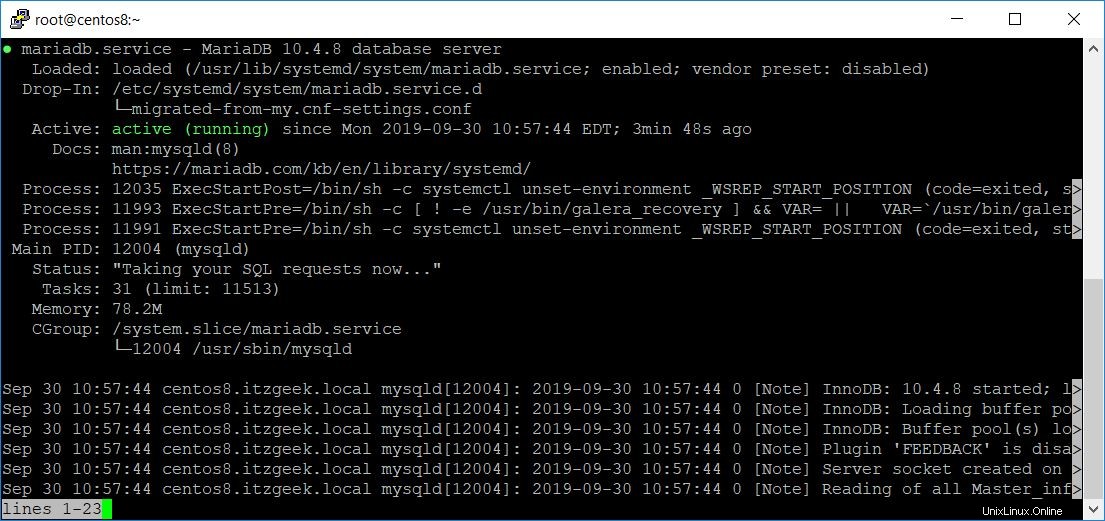
Verifica se MariaDB è in esecuzione o meno.
systemctl status mariadb
Installazione sicura di MariaDB
Utilizzare il comando mysql_secure_installation per eseguire la configurazione iniziale del server MariaDB. Si consiglia di eseguire questo comando nei server di produzione. Rimuove l'utente anonimo, testa il database e non consente l'accesso root remoto.
mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): << Just Press Enter
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody
can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] N << Disable Unix Socket Authendication to Enable Password Authentication
... skipping.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Change the root password? [Y/n] Y << Set MariaDB root password
New password: << Enter root password
Re-enter new password: << Re-Enter root password
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y << Remove Anonymous user
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y << Disallow root login remotely
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y << Remove test database
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y << Reload privilege tables
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Accedi a MariaDB
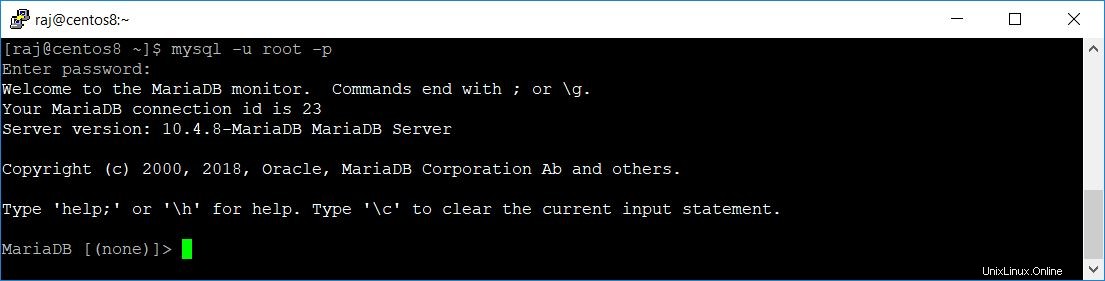
Accedi al server MariaDB con il comando seguente.
mysql -u root -pPassword richiesta
Conclusione
È tutto. In questo post, hai imparato come installare MariaDB su CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 ed eseguire la configurazione iniziale. Leggi gli articoli per principianti su MariaDB per saperne di più su come lavorare con MariaDB.