Nel business di oggi è sempre più necessario condividere spazi di lavoro, laboratori, strumenti e qualsiasi altro tipo di risorsa. Sfruttare al meglio le risorse disponibili è diventato un vantaggio competitivo per le aziende moderne.
Ogni azienda ha risorse limitate, quindi c'è una disputa sull'uso di queste risorse da parte di tutti i membri, questo è il punto, la disputa di queste risorse può causare problemi tra i dipendenti, usura delle relazioni e improduttività nell'organizzazione.
Questa discussione sembra essere lontana dalla tecnologia, tuttavia, per risolvere questo tipo di problemi, sono disponibili molti Software gratuiti e in questo articolo scrivo di uno strumento aziendale in grado di aiutare a organizzare l'uso delle risorse in modo equo ed efficace modo.
Panoramica del software
Booked è un software open source scritto in PHP e MySQL che aiuta organizzazioni e gruppi a gestire, registrare e tenere traccia in modo efficiente di risorse di qualsiasi tipo. Ti consente di creare pianificazioni in modo che gli utenti possano trovare le pianificazioni disponibili per l'uso delle risorse.
Prenotato consente di distribuire equamente le risorse attraverso l'uso delle quote. Consente inoltre di controllare l'utilizzo delle risorse tramite approvazioni di riserva. È inoltre possibile configurare un intervallo automatico tra le prenotazioni di una risorsa.
Prenotato include fantastiche funzionalità aziendali come supporto per molte lingue, basato sul Web, mobile first, sistema di reporting, promemoria, LDAP, Active Directory, file ical da integrare con i client di posta elettronica e altro ancora.
L'ambiente
Questo articolo copre l'installazione con prenotazione e la configurazione di base. Questo articolo è stato scritto in base al seguente ambiente:una VM Virtual Box con CENTOS 7 Minimal, 2 GB di RAM, 8 GB di HD e 2 interfacce di rete (solo host e NAT).
Sicurezza
Questo articolo non copre completamente questo argomento che è complesso ed esteso. Ha messo l'accento sul semplice S.O. configurazione e configurazione sistema Prenotato.
Preparazione
Supponendo che utilizzi una nuova installazione di Centos 7 Minimal, prima di installare Booked, esegui il comando seguente per aggiornare il sistema e installare pacchetti aggiuntivi:
yum update
Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Upgrade 39 Packages Total download size: 91 M Is this ok [y/d/N]: y
Installa il tuo editor di testo preferito o usa VI. In questo articolo utilizzo VIM, per installarlo esegui il seguente comando:
yum install vim
Installa il pacchetto WGET, esegui il seguente comando:
yum install wget
Installa il pacchetto UNZIP, esegui il seguente comando:
yum install unzip
Per configurare la rete, eseguire il comando seguente per aprire lo strumento NMTUI (Network Manager Text User Interface) e modificare le interfacce di rete e il nome host come si desidera:
nmtui
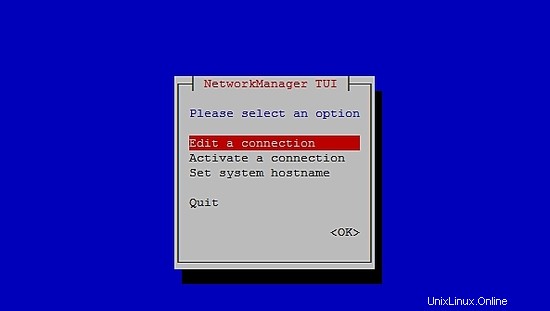
Dopo aver configurato le impostazioni di rete e il nome host su CentOS 7, esegui il comando seguente per applicare le modifiche:
service networks restart
Per verificare le informazioni di rete, eseguire il comando seguente:
ip addr
L'output è simile a questo:
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:67:bc:73 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.0.2.15/24 brd 10.0.2.255 scope global dynamic enp0s3
valid_lft 84631sec preferred_lft 84631sec
inet6 fe80::9e25:c982:1091:90eb/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: enp0s8: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:68:88:f3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.56.101/24 brd 192.168.56.255 scope global dynamic enp0s8
valid_lft 1044sec preferred_lft 1044sec
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe68:88f3/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Disabilita SELINUX (Security Enhanced Linux) su Centos 7, modifica il seguente file di configurazione:
vim /etc/selinux/config
"/etc/selinux/config" 14L, 547C# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=enforcing # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are prootected. # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted
Modifica il valore applicando della direttiva SELINUX ai disabilitati , salva il file e riavvia il server.
Per controllare lo stato di SELinux su Centos 7, eseguire il comando seguente:
getenforce
L'output deve essere:
Disabled
Per disabilitare FirewallD su Centos 7, esegui i seguenti comandi:
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
Per controllare lo stato del firewall su Centos 7, esegui il comando seguente:
systemctl status firewalld
Installa MariaDB, Apache e PHP su Centos 7
Per installare MariaDB su Centos 7, esegui il seguente comando:
yum -y install mariadb-server
Per avviare MariaDB, esegui il seguente comando:
systemctl start mariadb
Per aumentare la sicurezza di MariaDB, esegui il seguente comando:
/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
Imposta le opzioni in base al seguente output o usa le tue preferenze:
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):<Press Enter>
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] <Press Y>
Imposta la password di root:
New password: ******* Re-enter new password: ******* Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] <Press Y>
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] <Choose acording your needs>
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] <Press Y>
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] <Press Y>
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Configura MariaDB per l'avvio automatico con Centos 7:
systemctl enable mariadb.service
Per installare Apache, esegui il seguente comando:
yum install httpd
Per avviare Apache, esegui il seguente comando:
systemctl start httpd.service
Configura Apache per l'avvio automatico con Centos 7:
systemctl enable httpd.service
Per testare Apache, nel tuo browser web, digita gli indirizzi IP del tuo server. Se tutto va bene puoi vedere una pagina di prova:

Per installare PHP, esegui il seguente comando:
yum install php php-mysql
Riavvia Apache, esegui il seguente comando:
systemctl restart httpd.service
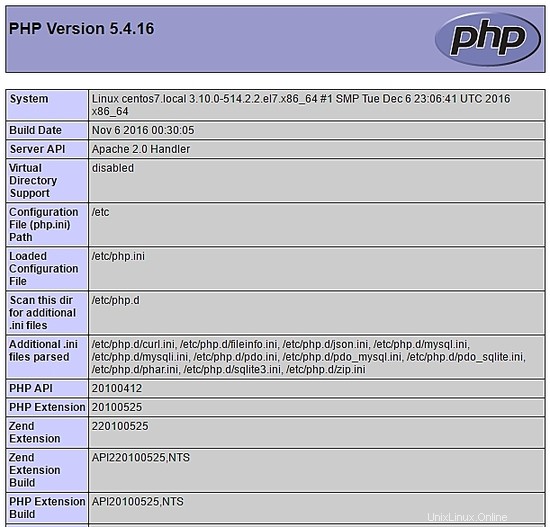
Per testare PHP crea un file phpinfo.php all'interno della directory /var/www/html con il seguente contenuto:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Ora puoi accedere a phpinfo.php tramite il browser con il seguente URL: http://[your-ip-addres]/phpinfo.php. Se tutto è a posto, puoi vedere la seguente pagina:
Configura il database tramite il terminale
Accedi a MariaDB tramite il terminale e crea il database bookedscheduler e l'utente utente_prenotato con diritti sufficienti per gestire questo database. Esegui i seguenti comandi da eseguire tramite il terminale:
mysql -u root -p
Crea programmatore prenotato banca dati:
MariaDB [(none)]> create database bookedscheduler;
Crea utente_prenotato su MariaDb:
CREATE USER 'booked_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_password';
Concedi le autorizzazioni all'utente booked_user a programmatore prenotato banca dati:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database.bookedscheduler TO 'booked_user'@'localhost';
Importa lo schema e i dati del database prenotato, dalla directory /var/www/html/booked/database_schema/, è necessario importare i seguenti file sql, create_schema.sql e creare-data.sql :
mysql -u root -p bookedscheduler < create-schema.sql
mysql -u root -p bookedscheduler < create-data.sql
Imposta il database tramite PHPMyAdmin
Installa PHPMyAdmin su Centos 7 (opzionale)
PHPMyAdmin è uno strumento per gestire i database mysql (mariaDB) in modo amichevole tramite un browser. Per installare phpmyadmin automaticamente, devi installare il repository Epel, esegui il seguente comando:
yum install epel-release
Ora puoi eseguire il seguente comando:
yum install phpmyadmin
Dopo l'installazione di PHPMyAdmin, dobbiamo configurarlo. Prima di tutto, fai una copia del file di configurazione e modifica il file phpMyAdmin.conf in /etc/httpd/conf.d/:
cp /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf.old
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf
Modifica i valori in base al tuo ambiente di rete, nel mio caso ho modificato le seguenti righe (17, 25, 34, 42). Il mio file di configurazione è simile a questo:
# phpMyAdmin - Web based MySQL browser written in php
#
# Allows only localhost by default
#
# But allowing phpMyAdmin to anyone other than localhost should be considered
# dangerous unless properly secured by SSL
Alias /phpMyAdmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Alias /phpmyadmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
<IfModule mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.4
<RequireAny>
Require ip 127.0.0.1
Require ip 192.168.56.1
Require ip ::1
</RequireAny>
</IfModule>
<IfModule !mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.2
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from 192.168.56.1
Allow from ::1
</IfModule>
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/setup/>
<IfModule mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.4
<RequireAny>
Require ip 127.0.0.1
Require ip ::1
</RequireAny>
</IfModule>
<IfModule !mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.2
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from 192.168.56.1
Allow from ::1
</IfModule>
</Directory>
# These directories do not require access over HTTP - taken from the original
# phpMyAdmin upstream tarball
#
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/libraries/>
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from None
</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/setup/lib/>
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from None
</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/setup/frames/>
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from None
</Directory>
# This configuration prevents mod_security at phpMyAdmin directories from
# filtering SQL etc. This may break your mod_security implementation.
#
#<IfModule mod_security.c>
# <Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/>
# SecRuleInheritance Off
# </Directory>
#</IfModule>
Riavvia Apache, esegui il seguente comando:
systemctl restart httpd.service
Ora puoi accedere a PHPMyAdmin tramite il browser con il seguente URL: http://[your-ip-addres]/phpMyAdmin/
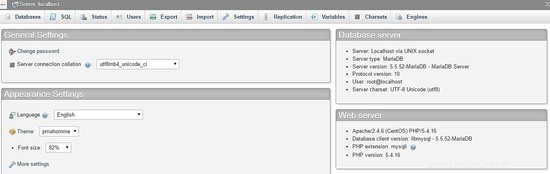
Usa la tua root account e la password precedentemente definita nell'installazione di MariaDB per creare il database e l'utente. Nella dashboard, seleziona Database opzione per creare un nuovo database:
Compila il modulo con il nome del database e seleziona crea .
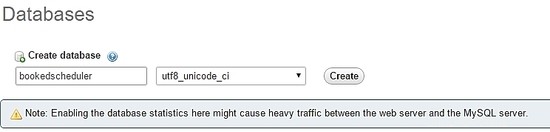
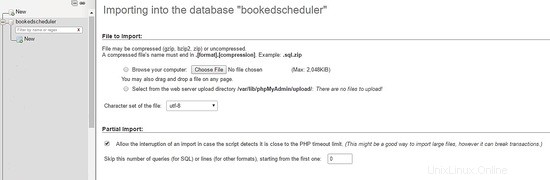
Per importare i dati del database, nel menu a sinistra, seleziona il programmatore prenotato database e Importa dalla dashboard di PHPMyAdmin, scegli i seguenti file, create-schema.sql (1) e create-data.sql (2), dai file di installazione e importalo.
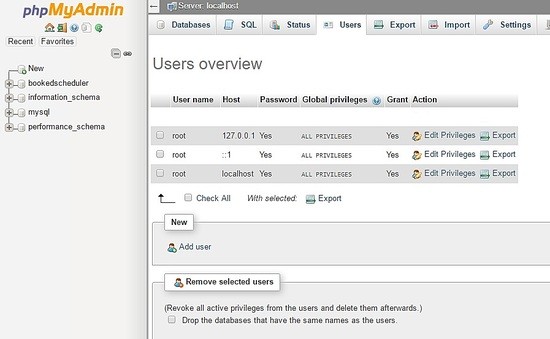
Crea l'utente utente_prenotato con i permessi per gestire bookedscheduler Banca dati. Nella dashboard di PHPMyAdmin, seleziona Utenti e Aggiungi :
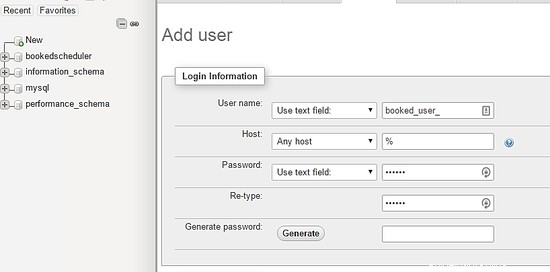
Nella schermata di creazione dell'utente, compila i campi con il database degli utenti (utente_prenotato), imposta una password e seleziona Vai a fine pagina:
Per impostare i privilegi per utente_prenotato su programmatore prenotato database, seleziona programmatore prenotato da un elenco di database e seleziona Vai:
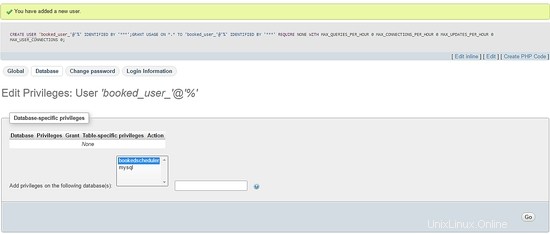
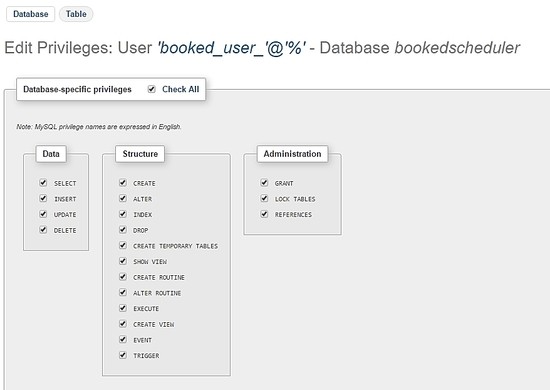
Nella schermata dei privilegi, seleziona l'opzione Seleziona tutto e Vai :
Installazione di Booked Scheduler Centos 7
Abbiamo due modi per installare Booked Scheduler, manualmente o automaticamente. Questo articolo copre solo l'installazione manuale. Per installare Booked Scheduler su Centos 7, vai alla directory /tmp e scarica il codice sorgente:
wget https://ufpr.dl.sourceforge.net/project/phpscheduleit/Booked/2.6/booked-2.6.5.zip
Decomprimi il file nella directory /var/www/html, esegui il comando seguente:
unzip booked-2.6.5.zip -d /var/www/html/
Modifica le autorizzazioni del file decompresso.
cd /var/www/html/
chown -R apache:apache /booked
Imposta il file di configurazione in /var/www/html/booked/config. Crea una copia del file config.dist.php in config.php e modifica i blocchi del file di configurazione (è il mio file di configurazione):
cp config.dist.php config.php
Modifica i valori in base al nostro ambiente, qui presento le impostazioni principali da modificare e tieni presente che l'indirizzo email sarà l'amministratore di sistema dopo la prima registrazione:
<?php
/**
Copyright 2011-2016 Nick Korbel
This file is part of Booked Scheduler.
Booked Scheduler is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
Booked Scheduler is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with Booked Scheduler. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT);
//ini_set('display_errors', 1);
//ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
/**
* Application configuration
*/
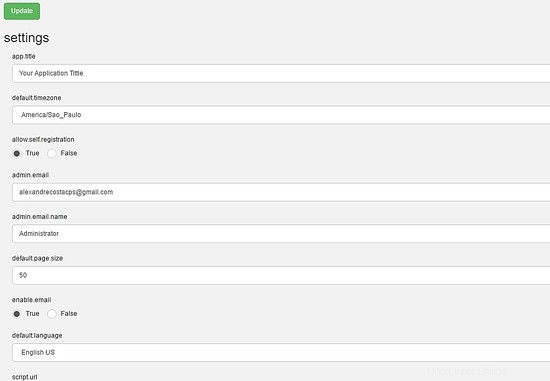
$conf['settings']['app.title'] = 'Booked Scheduler'; // application title
$conf['settings']['default.timezone'] = 'America/Chicago'; // Change your time zone - look up here http://php.net/manual/en/timezones.php
$conf['settings']['allow.self.registration'] = 'true'; // if users can register themselves
$conf['settings']['admin.email'] = '[email protected]'; // fill with the email address of admin user
$conf['settings']['admin.email.name'] = 'Booked Administrator'; // name to be used in From: field when sending automatic emails
$conf['settings']['default.page.size'] = '50'; // number of records per page
$conf['settings']['enable.email'] = 'true'; // global configuration to enable if any emails will be sent
$conf['settings']['default.language'] = 'en_us'; Change acording to your language // find your language in the lang directory
$conf['settings']['script.url'] = 'http://[your-ip-address]/Web'; // public URL to the Web directory of this instance. this is the URL that appears when you are logging in. leave http: or https: off to auto-detect
$conf['settings']['image.upload.directory'] = 'Web/uploads/images'; // full or relative path to where images will be stored
$conf['settings']['image.upload.url'] = 'uploads/images'; // full or relative path to show uploaded images from
$conf['settings']['cache.templates'] = 'true'; // true recommended, caching template files helps web pages render faster
$conf['settings']['use.local.jquery'] = 'false'; // false recommended, delivers jQuery from Google CDN, uses less bandwidth
$conf['settings']['registration.captcha.enabled'] = 'true'; // recommended. unless using recaptcha this requires php_gd2 enabled in php.ini
$conf['settings']['registration.require.email.activation'] = 'true'; // requires enable.email = true
$conf['settings']['registration.auto.subscribe.email'] = 'false'; // requires enable.email = true
$conf['settings']['registration.notify.admin'] = 'true'; // whether the registration of a new user sends an email to the admin (ala phpScheduleIt 1.2)
$conf['settings']['inactivity.timeout'] = '30'; // minutes before the user is automatically logged out
$conf['settings']['name.format'] = '{first} {last}'; // display format when showing user names
$conf['settings']['css.extension.file'] = ''; // full or relative url to an additional css file to include. this can be used to override the default style
$conf['settings']['disable.password.reset'] = 'false'; // if the password reset functionality should be disabled
$conf['settings']['home.url'] = 'your-intranet-portal-url'; // the url to open when the logo is clicked
$conf['settings']['logout.url'] = 'your-intranet-portal-url'; // the url to be directed to after logging out
$conf['settings']['default.homepage'] = '1'; // the default homepage to use when new users register (1 = Dashboard, 2 = Schedule, 3 = My Calendar, 4 = Resource Calendar)
$conf['settings']['schedule']['use.per.user.colors'] = 'false'; // color reservations by user
$conf['settings']['schedule']['show.inaccessible.resources'] = 'true'; // whether or not resources that are inaccessible to the user are visible
$conf['settings']['schedule']['reservation.label'] = '{name}'; // format for what to display on the reservation slot label. Available properties are: {name}, {title}, {description}, {email}, {phone}, {organization}, {position}, {startdate}, {enddate} {resourcename} {participants} {invitees} {reservationAttributes}. Custom attributes can be added using att with the attribute id. For example {att1}
$conf['settings']['schedule']['hide.blocked.periods'] = 'false'; // if blocked periods should be hidden or shown
/**
* ical integration configuration
*/
$conf['settings']['ics']['require.login'] = 'true'; // recommended, if the user must be logged in to access ics files
$conf['settings']['ics']['subscription.key'] = ''; // must be set to allow webcal subscriptions
$conf['settings']['ics']['import'] = 'false'; // enable iCal import
$conf['settings']['ics']['import.key'] = ''; // it's recommended to set this key when iCal import is enabled
/**
* Privacy configuration - Set up here your business rules
*/
$conf['settings']['privacy']['view.schedules'] = 'true'; // if unauthenticated users can view schedules
$conf['settings']['privacy']['view.reservations'] = 'false'; // if unauthenticated users can view reservations
$conf['settings']['privacy']['hide.user.details'] = 'false'; // if personal user details should be displayed to non-administrators
$conf['settings']['privacy']['hide.reservation.details'] = 'false'; // if reservation details should be displayed to non-administrators
$conf['settings']['privacy']['allow.guest.reservations'] = 'false'; // if reservations can be made by users without a Booked account, if true this overrides schedule and resource visibility
/**
* Reservation specific configuration
*/
$conf['settings']['reservation']['start.time.constraint'] = 'future'; // when reservations can be created or edited. options are future, current, none
$conf['settings']['reservation']['updates.require.approval'] = 'false'; // if updates to previously approved reservations require approval again
$conf['settings']['reservation']['prevent.participation'] = 'false'; // if participation and invitation options should be removed
$conf['settings']['reservation']['prevent.recurrence'] = 'false'; // if recurring reservations are disabled for non-administrators
$conf['settings']['reservation']['enable.reminders'] = 'false'; // if reminders are enabled. this requires email to be enabled and the reminder job to be configured
$conf['settings']['reservation']['allow.guest.participation'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation']['allow.wait.list'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation']['checkin.minutes.prior'] = '5';
/**
* Email notification configuration
*/
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['resource.admin.add'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['resource.admin.update'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['resource.admin.delete'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['resource.admin.approval'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['application.admin.add'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['application.admin.update'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['application.admin.delete'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['application.admin.approval'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['group.admin.add'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['group.admin.update'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['group.admin.delete'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['reservation.notify']['group.admin.approval'] = 'false';
/**end business rules
* File upload configuration
*/
$conf['settings']['uploads']['enable.reservation.attachments'] = 'false'; // if reservation attachments can be uploaded
$conf['settings']['uploads']['reservation.attachment.path'] = 'uploads/reservation'; // full or relative (to the root of your installation) filesystem path to store reservation attachments
$conf['settings']['uploads']['reservation.attachment.extensions'] = 'txt,jpg,gif,png,doc,docx,pdf,xls,xlsx,ppt,pptx,csv'; // comma separated list of file extensions that users are allowed to attach. leave empty to allow all extensions
/**
* Database configuration
*/
$conf['settings']['database']['type'] = 'mysql';
$conf['settings']['database']['user'] = 'booked_user'; // database user with permission to the booked database
$conf['settings']['database']['password'] = 'your_password'; fill with the booked_user password
$conf['settings']['database']['hostspec'] = '127.0.0.1'; // ip, dns or named pipe
$conf['settings']['database']['name'] = 'bookedscheduler';
/**TIP: if you have problems to conect to database, please, try with the user and passord of root, if it works, go back to user database permitions.
* Mail server configuration
*/To e-mail configurarion I need to use a relay to my e-mail server and in my server I instaled postfix and configurate it to send e-mails
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['mailer'] = 'mail'; // options are 'mail', 'smtp' or 'sendmail'
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['smtp.host'] = 'your-mx'; // 'smtp.company.com'
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['smtp.port'] = '25';
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['smtp.secure'] = ''; // options are '', 'ssl' or 'tls'
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['smtp.auth'] = 'true'; // options are 'true' or 'false'
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['smtp.username'] = '[email protected]';
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['smtp.password'] = 'your-password';
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['sendmail.path'] = '/usr/sbin/sendmail';
$conf['settings']['phpmailer']['smtp.debug'] = 'false';
/**
* Plugin configuration. For more on plugins, see readme_installation.html
*/
$conf['settings']['plugins']['Authentication'] = '';
$conf['settings']['plugins']['Authorization'] = '';
$conf['settings']['plugins']['Permission'] = '';
$conf['settings']['plugins']['PostRegistration'] = '';
$conf['settings']['plugins']['PreReservation'] = '';
$conf['settings']['plugins']['PostReservation'] = '';
/**
* Installation settings
*/
$conf['settings']['install.password'] = ''; //just to automated instalation
/**
* Pages
*/
$conf['settings']['pages']['enable.configuration'] = 'true';
/**
* API
*/
$conf['settings']['api']['enabled'] = 'false';
/**
* ReCaptcha
*/
$conf['settings']['recaptcha']['enabled'] = 'false';
$conf['settings']['recaptcha']['public.key'] = '';
$conf['settings']['recaptcha']['private.key'] = '';
/**
*/
$conf['settings']['email']['default.from.address'] = 'your-email-address';
$conf['settings']['email']['default.from.name'] = 'your-system-name';
/**
* Reports
*/
$conf['settings']['reports']['allow.all.users'] = 'false';
/**
* Account Password Rules
*/
$conf['settings']['password']['minimum.letters'] = '6';
$conf['settings']['password']['minimum.numbers'] = '0';
$conf['settings']['password']['upper.and.lower'] = 'false';
/**
* Label display settings
*/
$conf['settings']['reservation.labels']['ics.summary'] = '{title}';
$conf['settings']['reservation.labels']['ics.my.summary'] = '{title}';
$conf['settings']['reservation.labels']['rss.description'] = '<div><span>Start</span> {startdate}</div><div><span>End</span> {enddate}</div><div><span>Organizer</span> {name}</div><div><span>Description</span> {description}</div>';
$conf['settings']['reservation.labels']['my.calendar'] = '{resourcename} {title}';
$conf['settings']['reservation.labels']['resource.calendar'] = '{name}';
$conf['settings']['reservation.labels']['reservation.popup'] = ''; // Format for what to display in reservation popups. Possible values: {name} {dates} {title} {resources} {participants} {accessories} {description} {attributes}. Custom attributes can be added using att with the attribute id. For example {att1}
/**
* Security header settings
*/
$conf['settings']['security']['security.headers'] = 'false'; // Enable the following options
$conf['settings']['security']['security.strict-transport'] = 'true';
$conf['settings']['security']['security.x-frame'] = 'deny';
$conf['settings']['security']['security.x-xss'] = '1; mode=block';
$conf['settings']['security']['security.x-content-type'] = 'nosniff';
$conf['settings']['security']['security.content-security-policy'] = "default-src 'self'"; // Requires careful tuning (know what your doing)
/**
* Google Analytics settings
*/
$conf['settings']['google.analytics']['tracking.id'] = ''; // if set, Google Analytics tracking code will be added to every page in Booked
$conf['settings']['authentication']['allow.facebook.login'] = 'true';
$conf['settings']['authentication']['allow.google.login'] = 'true';
$conf['settings']['authentication']['required.email.domains'] = '';
/**
* Credits functionality
*/
$conf['settings']['credits']['enabled'] = 'false';
Configura l'interfaccia web del pianificatore prenotato
Accedi al seguente indirizzo http://your-ipaddress/Web/index.php, se tutto funziona correttamente, vedrai la seguente schermata:
Seleziona l'opzione Registrati per creare un account amministratore, ricorda, usa l'indirizzo e-mail precedentemente configurato nel file config.php.
Dopo aver creato il tuo account, vai alla schermata di accesso e autenticati. A dashboard will be load, like this image:
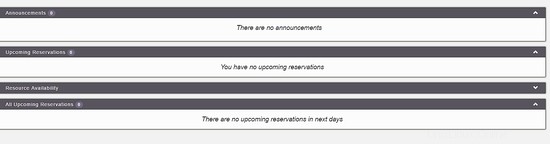
On the main menu, you can config all system, select Application Management :

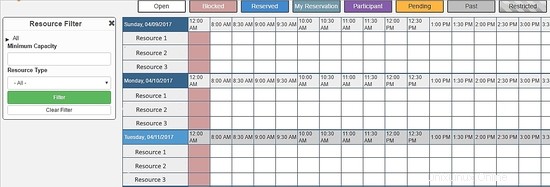
Through this menu, you can configure all resources of Booked Scheduler, to change the config.php, select the Application Configuration :
This article is a small overview about Booked Scheduler, this software has a lot of amazing features who can help any environment to provide a rational use of resources.

I hope this article can introduce you to the software, in case you have any problem with the installation, feel free to ask questions. If you want to get more information about Booked Scheduler access http://www.bookedscheduler.com/.