Per installare Centos 7 OS segui i passaggi seguenti:
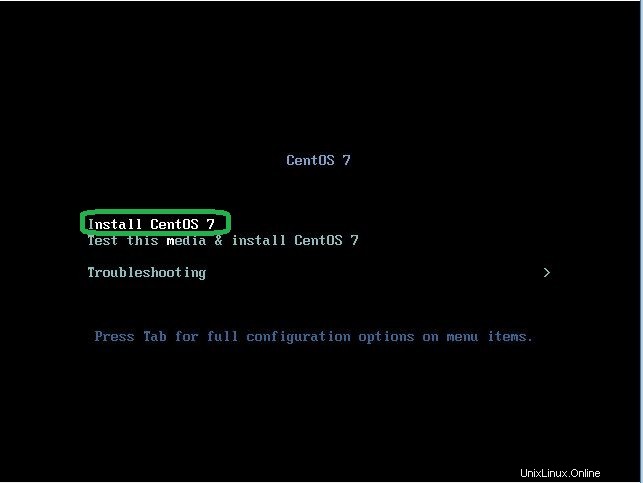
- Inserisci il disco di installazione di Centos sul server o sul computer, quindi seleziona "Installa Centos 7" e premi il tasto Invio per procedere.
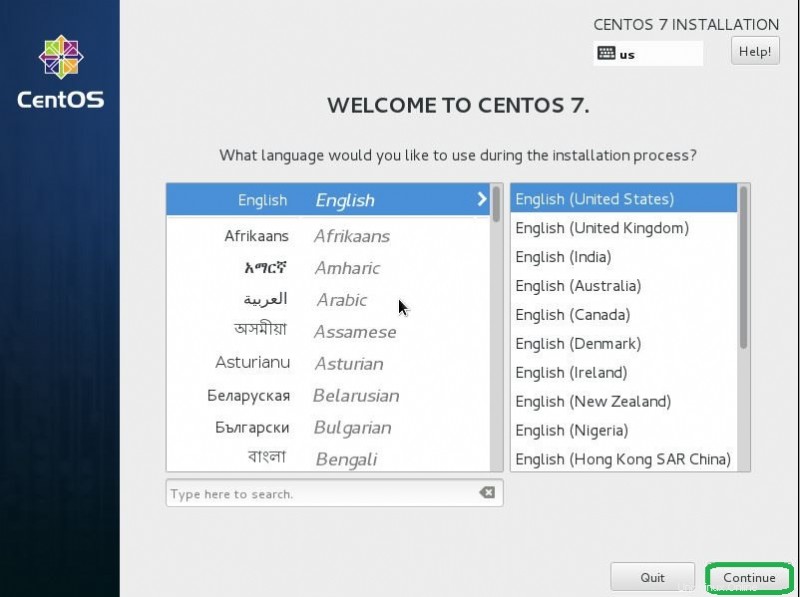
- Seleziona la lingua che desideri utilizzare e fai clic su continua.
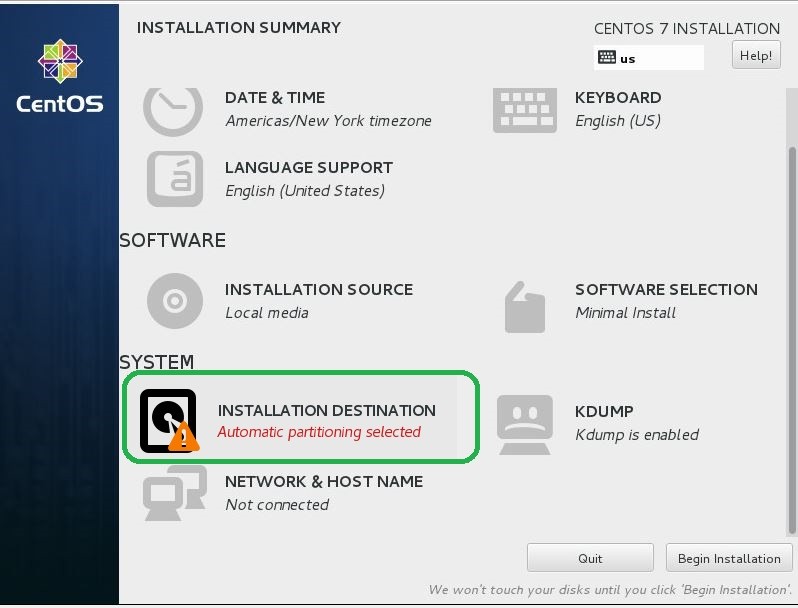
- Quindi, fai clic sull'icona DESTINAZIONE DELL'INSTALLAZIONE.
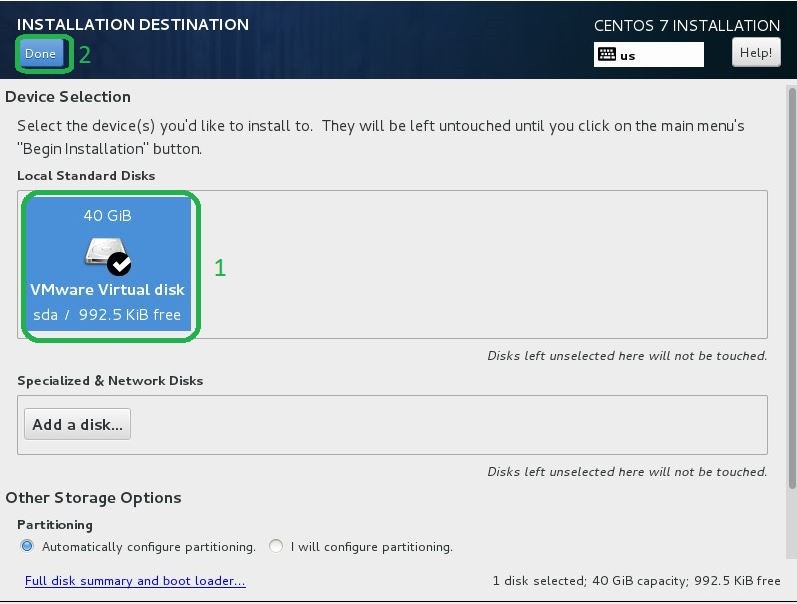
- Seleziona il disco di installazione. Fare clic sull'icona del disco che si desidera installare e quindi fare clic sul pulsante Fine in alto a sinistra per procedere.
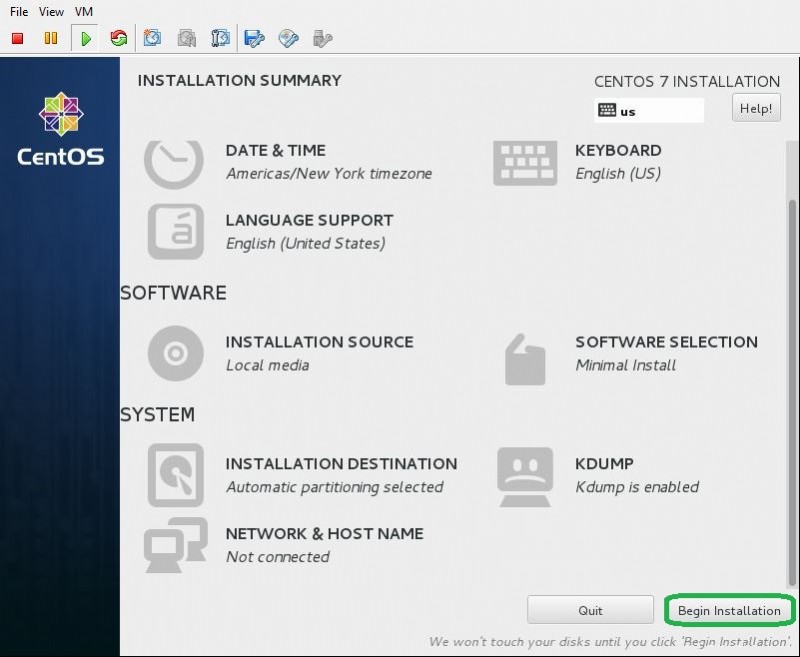
- Se è tutto a posto, fai clic su Inizia installazione e procedi con il prossimo.
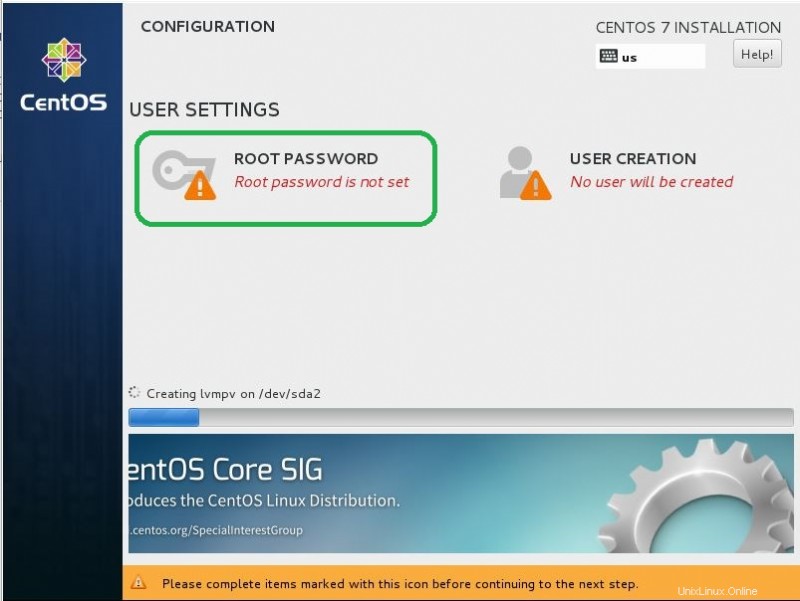
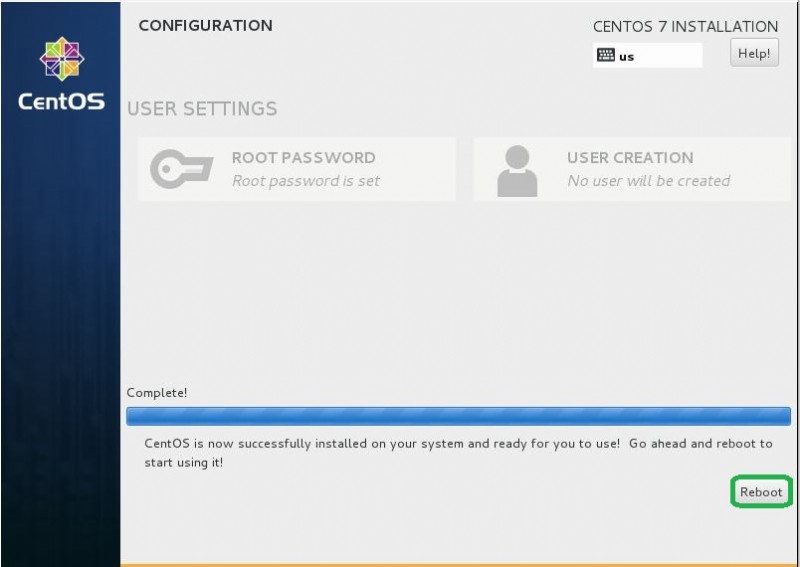
- L'installazione viene avviata ed è richiesta per impostare la password di root. Fai clic su Password di root vai alla configurazione.
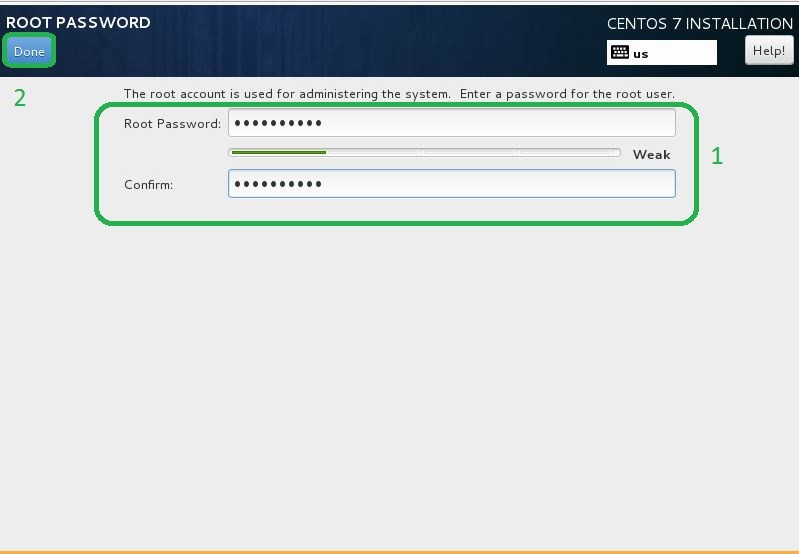
- Nelle impostazioni della password di root, inserisci la password che preferisci e fai clic sul pulsante Fine per terminare come segue.
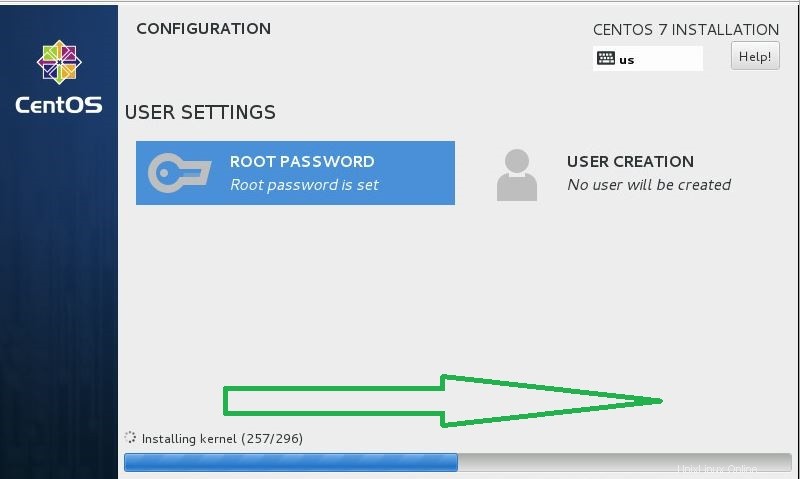
- Fai clic sul pulsante Riavvia, Al termine dell'installazione.
- Dopo il riavvio, viene visualizzata la richiesta di accesso come segue e accedi con utente e password root.
Puoi seguire le diapositive di seguito per vedere tutti questi passaggi:
Comandi di base:server di aggiornamento, controllo del servizio e così via
Dopo aver installato il sistema operativo, è necessario aggiornare il server. Per farlo, segui i comandi seguenti:
[root@thehackertips ~]# yum -y update
Per elencare il servizio in esecuzione su Centos 7, esegui i comandi seguenti:
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl -t service UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION auditd.service loaded active running Security Auditing Service crond.service loaded active running Command Scheduler dbus.service loaded active running D-Bus System Message Bus firewalld.service loaded active running firewalld - dynamic firewall getty@tty1.service loaded active running Getty on tty1 kdump.service loaded active exited Crash recovery kernel arming kmod-static-nodes.service loaded active exited Create list of required stati lvm2-lvmetad.service loaded active running LVM2 metadata daemon lvm2-monitor.service loaded active exited Monitoring of LVM2 mirrors, s lvm2-pvscan@8:2.service loaded active exited LVM2 PV scan on device 8:2 network.service loaded active exited LSB: Bring up/down networking NetworkManager.service loaded active running Network Manager ntpd.service loaded active running Network Time Service polkit.service loaded active running Authorization Manager postfix.service loaded active running Postfix Mail Transport Agent rhel-dmesg.service loaded active exited Dump dmesg to /var/log/dmesg rhel-import-state.service loaded active exited Import network configuration rhel-readonly.service loaded active exited Configure read-only root supp rsyslog.service loaded active running System Logging Service sshd.service loaded active running OpenSSH server daemon systemd-journald.service loaded active running Journal Service systemd-logind.service loaded active running Login Service systemd-random-seed.service loaded active exited Load/Save Random Seed systemd-remount-fs.service loaded active exited Remount Root and Kernel File systemd-sysctl.service loaded active exited Apply Kernel Variables systemd-t...etup-dev.service loaded active exited Create static device nodes in systemd-t...es-setup.service loaded active exited Create Volatile Files and Dir systemd-udev-trigger.service loaded active exited udev Coldplug all Devices systemd-udevd.service loaded active running udev Kernel Device Manager systemd-update-utmp.service loaded active exited Update UTMP about System Rebo systemd-u...sessions.service loaded active exited Permit User Sessions systemd-v...le-setup.service loaded active exited Setup Virtual Console tuned.service loaded active running Dynamic System Tuning Daemon LOAD = Reflects whether the unit definition was properly loaded. ACTIVE = The high-level unit activation state, i.e. generalization of SUB. SUB = The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type. 33 loaded units listed. Pass --all to see loaded but inactive units, too. To show all installed unit files use 'systemctl list-unit-files'.
Per elencare tutti i servizi, esegui i comandi seguenti:
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl list-unit-files -t service UNIT FILE STATE auditd.service enabled autovt@.service disabled blk-availability.service disabled brandbot.service static console-getty.service disabled console-shell.service disabled cpupower.service disabled crond.service enabled dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service enabled dbus-org.freedesktop.hostname1.service static dbus-org.freedesktop.locale1.service static dbus-org.freedesktop.login1.service static dbus-org.freedesktop.machine1.service static
Per avviare, riavviare, interrompere o mostrare lo stato dei servizi utilizzando questi comandi:
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl start firewalld
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl restart firewalld
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl status firewalld
Aggiungi un nuovo utente e imposta la password
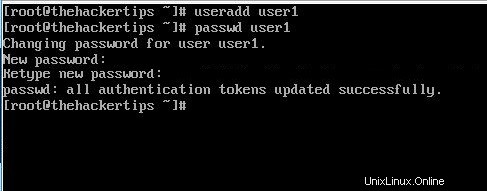
Per creare un nuovo utente e impostare la password su centos 7 segui i comandi seguenti:
[root@thehackertips ~]# useradd user1 [root@thehackertips ~]# passwd user1 Changing password for user user1. New password:# set password Retype new password:# confirm passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. [root@thehackertips ~]# exit
Puoi passare da root a user1 o user1 a root. Per farlo, segui i comandi seguenti:
[root@thehackertips ~]# su - user1 Last login: Tue Sep 3 09:37:36 EDT 2019 om tty1 [root@thehackertips ~]# su - Password: # type the root password Last login: Tue Sep 3 09:37:08 EDT 2019 om tty1 [root@thehackertips ~]#
Reimposta password utente/root
Per reimpostare la password su Centos 7 è necessario utilizzare i comandi seguenti:
- sudo passwd root # se è un utente root
- sudo passwd utente1 # qualsiasi altro utente
- passwd # se sei già loggato e vuoi cambiare la tua password
Imposta nome host
Per modificare il nome host su Centos 7 puoi utilizzare questi metodi:
- Opzione 1:modifica il file hostname con sudo vi /etc/hostname
- Opzione 2:hostnamectl set-hostname thehackertips.com # imposta il nome host in modo permanente
- Opzione 3:nome host thehackertips.com # questo andrà via dopo il riavvio
Per guardare lo stato del nome host usando questo comando
[root@thehackertips ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: thehackertips.com
Icon name: computer
Chassis: n/a
Machine ID: afa6c9d874624941b30b5caf02c5e24a
Boot ID: 8e08002be86e4355a82b9b343810ef38
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:7
Kernel: Linux 3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64
Architecture: x86_64 Modifica le impostazioni di rete
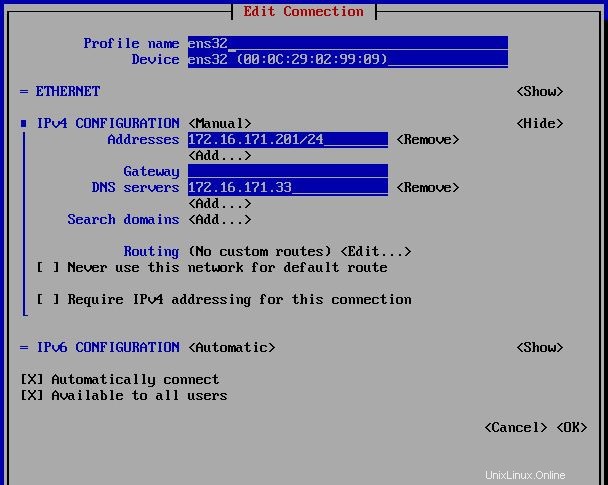
Uno dei modi per impostare l'indirizzo IP statico sul server consiste nell'usare i comandi nmcli. Per vedere lo stato dell'interfaccia Puoi usare questi comandi:
[root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli d DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION ens32 ethernet connected ens32 lo loopback unmanaged -- [root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli d show ens32 GENERAL.DEVICE: ens32 GENERAL.TYPE: ethernet GENERAL.HWADDR: 00:0C:29:02:99:09 GENERAL.MTU: 1500 GENERAL.STATE: 100 (connected) GENERAL.CONNECTION: ens32 GENERAL.CON-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/0 WIRED-PROPERTIES.CARRIER: on IP4.ADDRESS[1]: 172.16.171.201/24 IP4.GATEWAY: IP4.DNS[1]: 172.16.171.33 IP6.ADDRESS[1]: fe80::20c:29ff:fe02:9909/64 IP6.GATEWAY: [root@thehackertips ~]#
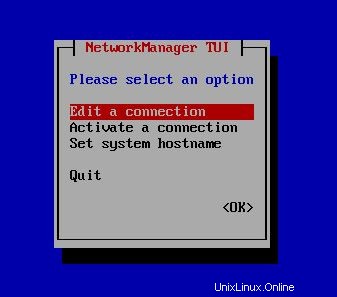
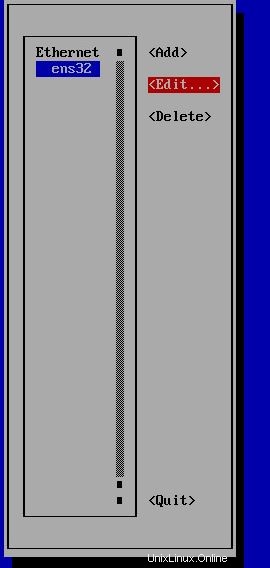
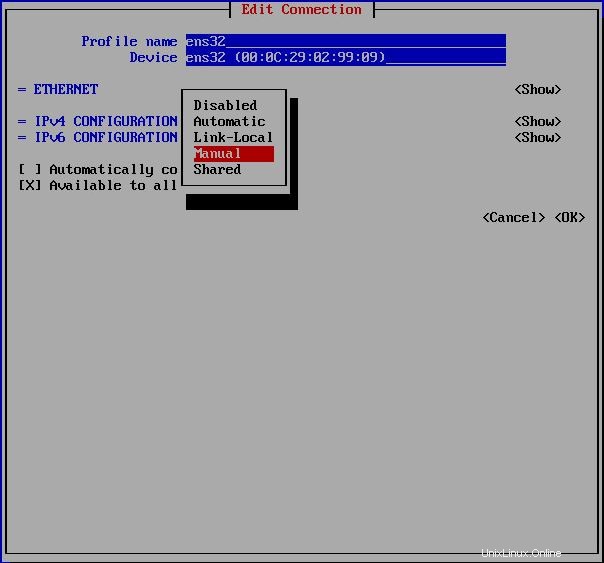
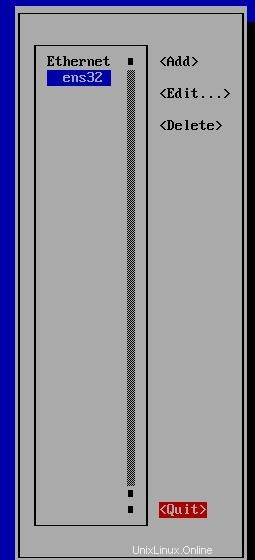
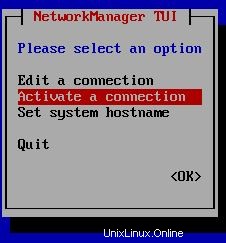
Per impostare un nuovo indirizzo IP puoi inserire nmtui comando su CLI e seguire i passaggi come di seguito. Nell'ultimo passaggio devi inserire nmtui e Attiva una connessione :
Inoltre puoi impostare l'indirizzo IP con nmcli comandi come di seguito:
# Set IP address [root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli c modify ens32 ipv4.addresses 172.16.171.201/24 # Set default gateway [root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli c modify ens32 ipv4.gateway 172.16.171.1 # Set the DNS [root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli c modify ens32 ipv4.dns 172.16.171.33 # Set manual IP address [root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli c modify ens32 ipv4.method manual # If you want to set DHCP IP address [root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli c modify ens32 ipv4.method dhcp # to restart interface [root@thehackertips ~]# nmcli c down ens32 ; nmcli c up
Per controllare l'indirizzo IP:
[root@thehackertips ~]# ip addr
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens32: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:02:99:09 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.16.171.201/24 brd 172.16.171.255 scope global ens32
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe02:9909/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever