
Verificato e testato il 27/02/2021
Introduzione
In questo articolo, ti guideremo attraverso la creazione di un server di posta completo su Ubuntu 20.04 con Postfix. Costruire un server di posta Linux da zero può essere un processo doloroso a meno che tu non lo faccia giorno dopo giorno, ma ti mostreremo come farlo nel modo più indolore possibile.
Un server di posta di solito è costituito da una gamma di pacchetti diversi che gestiscono SMTP, POP3/IMAP, archiviazione della posta e attività relative allo spam e devono parlare tutti insieme. Ecco uno schema dei pacchetti e degli obiettivi per questo articolo di istruzioni.
Schema di pacchetti e passaggi di configurazione
1 – Preparazione di base del server
2 – Creazione del server Web LAMP
3 – Configurazione di PHP
4 – Configurazione di Apache2
5 – Installazione e configurazione di Memcached
6 – Installazione i pacchetti del server di posta
7 – Creazione di un database MySQL per il server di posta
8.1 – Installazione di Postfix Admin
8.2 – Configurazione di Postfix Admin
9 – Aggiunta di account utente (caselle di posta) a Postfix Admin
10 – Creare un utente di sistema per gestire le directory di posta virtuale
11 – Configurazione di Dovecot
12 – Configurazione di filtri antispam e antivirus
13 – Configurazione di Postfix
14 – Ricerca DNS inversa
15 – Installa RoundCube Webmail
Prerequisiti
– Server Ubuntu 20.04 completamente aggiornato, se non hai un server Ubuntu in esecuzione su un server come quelli dell'hosting Linux VPS di Atlantic.net.
– Accesso al nome di dominio per il quale configurerai la posta (usaremo “email.linuxbuz.com ” negli esempi in questo articolo).
.
1 – Preparazione di base del server
L'installazione di base di Ubuntu include un set limitato di pacchetti, quindi la prima cosa che vogliamo fare è installare gli strumenti che utilizzeremo per completare tutte le attività.
Innanzitutto, assicurati di aver effettuato l'accesso come account utente root.
sudo su -
Ora installiamo gli strumenti di base in modo da poter scaricare file e modificare facilmente i file di configurazione.
apt-get install wget nano ssl-cert
- wget :pacchetto per il recupero di file tramite HTTP, HTTPS e FTP, i protocolli Internet più diffusi.
- nano :editor di testo a riga di comando con controlli facili da usare.
- certificato SSL :pacchetto che abilita la possibilità di creare certificati SSL.
Successivamente, aggiorneremo il nome host e il nome di dominio del server in modo che quando invii un'e-mail corrisponda al record DNS del puntatore inverso che abbiamo impostato con il tuo provider di hosting. Aggiorneremo anche il /etc/hostname file. Assicurati di sostituire esempio con il tuo nome host e dominio reale.
hostnamectl set-hostname email.linuxbuz.com
Ora modificheremo manualmente il /etc/hosts file di configurazione in modo che corrisponda al nome che abbiamo appena inserito.
nano /etc/hosts
Modifica la prima riga e aggiungi il tuo FQDN (nome di dominio completo) subito dopo l'indirizzo IP 127.0.0.1.
127.0.0.1 email.linuxbuz.com localhost
Ora aggiorneremo il certificato SSL predefinito sul server in modo che corrisponda al nostro nuovo nome host. Se hai acquistato un certificato SSL per il tuo server di posta, puoi saltare questo passaggio.
make-ssl-cert generate-default-snakeoil --force-overwrite
Questo comando dice al server di rigenerare il certificato SSL di sistema predefinito e lo costringe a sovrascrivere i file CRT e KEY originali.
Ora abbiamo completato la preparazione di base del server e possiamo passare all'installazione dei nostri servizi di server web.
[Torna su]
2 – Realizza il server web LAMP
Durante questo passaggio, installeremo i pacchetti "LAMP". LAMP sta per Linux, Apache, MySQL e PHP. Questi pacchetti combinati consentiranno al tuo server di fornire servizi Web dinamici con connettività MySQL.
Innanzitutto, installiamo i pacchetti. Questa è chiamata installazione di un pacchetto di attività.
apt-get install lamp-server^
Per visualizzare un elenco dei pacchetti inclusi in questa installazione di gruppo, puoi eseguire quanto segue:
tasksel --task-packages lamp-server
Dopo aver installato tutti i pacchetti, saremo pronti per installare alcuni moduli PHP aggiuntivi. Questi moduli aggiuntivi consentiranno al tuo server di supportare APC User Cache per PHP 5, memcached, cURL, un parser XML e l'elaborazione di immagini GD.
apt-get install php-apcu php-memcache php-curl php-mbstring php-gd php-xml php-imap php-xmlrpc libdbi-perl libdbd-mysql-perl -y
Successivamente, dovrai impostare la password root di MySQL e proteggere l'installazione di MySQL. Puoi farlo con il seguente comando:
mysql_secure_installation
Rispondi a tutte le domande come mostrato di seguito:
New password: Re-enter new password: Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
Quindi, accedi a MySQL e modifica la politica della password su bassa:
mysql -u root -p SET GLOBAL validate_password.policy = 0; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
[Torna su]
3 – Configura PHP
Ora aggiorneremo la configurazione di PHP. La configurazione predefinita è generalmente sufficiente per la maggior parte dei sistemi; tuttavia, vogliamo assicurarci che PHP non esponga le informazioni a potenziali aggressori. Modificheremo il file /etc/php/7.4/apache2/php.ini .
nano /etc/php/7.4/apache2/php.ini
Individua la variabile expose_php e aggiorna il valore da On su Off . Con nano, puoi cercare premendo CTRL-W e quindi inserisci la parola da cercare.
367 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; 368 ; Miscellaneous ; 369 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; 370 371 ; Decides whether PHP may expose the fact that it is installed on the server 372 ; (e.g. by adding its signature to the Web server header). It is no security 373 ; threat in any way, but it makes it possible to determine whether you use PHP 374 ; on your server or not. 375 ; http://php.net/expose-php 376 expose_php = Off 377
[Torna su]
4 – Configura Apache2
Siamo ora pronti per passare alla personalizzazione della configurazione dei servizi web di Apache. Il risultato finale per Apache è che servirà un unico sito Web con un paio di applicazioni Web in esecuzione:Webmail (RoundCube) e Postfix Admin. Tutto il traffico verrà indirizzato ai servizi Web HTTPS (protetti).
Innanzitutto, ridurremo al minimo le informazioni che Apache espone al pubblico. Usando nano, modificheremo il file di configurazione /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf .
nano /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf
Cerca la variabile di configurazione ServerTokens e imposta il valore da OS a Prod .
# ServerTokens # This directive configures what you return as the Server HTTP response # Header. The default is 'Full' which sends information about the OS-Type # and compiled in modules. # Set to one of: Full | OS | Minimal | Minor | Major | Prod # where Full conveys the most information, and Prod the least. #ServerTokens Minimal ServerTokens Prod #ServerTokens Full
Ora cerca la variabile di configurazione ServerSignature e imposta il valore da On su Off .
# Optionally add a line containing the server version and virtual host # name to server-generated pages (internal error documents, FTP directory # listings, mod_status and mod_info output etc., but not CGI generated # documents or custom error documents). # Set to "EMail" to also include a mailto: link to the ServerAdmin. # Set to one of: On | Off | EMail ServerSignature Off #ServerSignature On
Ora puoi salvare ed uscire da questo file di configurazione.
Ora abiliteremo i moduli aggiuntivi rewrite e ssl in Apache in modo da poter reindirizzare il traffico HTTP predefinito alla porta HTTPS e supportare i certificati SSL all'interno di Apache.
a2enmod rewrite ssl a2ensite default-ssl
Passiamo ora alla personalizzazione della configurazione del sito web. Questi file si trovano nella directory /etc/apache2/sites-available . Aggiorneremo i file di configurazione predefiniti esistenti per supportare i servizi SSL.
Innanzitutto, modifica il file di configurazione 000-default.conf . Puoi sostituire la configurazione esistente con la seguente, basta sostituire il ServerName variabile con il tuo nome host.
nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
# The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that
# the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
# redirection URLs. In the context of virtual hosts, the ServerName
# specifies what hostname must appear in the request's Host: header to
# match this virtual host. For the default virtual host (this file) this
# value is not decisive as it is used as a last resort host regardless.
# However, you must set it for any further virtual host explicitly.
ServerName email.linuxbuz.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
<Directory "/var/www/html">
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
# Available loglevels: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
# error, crit, alert, emerg.
# It is also possible to configure the loglevel for particular
# modules, e.g.
LogLevel info ssl:warn
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
# For most configuration files from conf-available/, which are
# enabled or disabled at a global level, it is possible to
# include a line for only one particular virtual host. For example the
# following line enables the CGI configuration for this host only
# after it has been globally disabled with "a2disconf".
#Include conf-available/serve-cgi-bin.conf
</VirtualHost> Ora puoi salvare ed uscire da questo file di configurazione.
Se non hai acquistato il tuo certificato SSL, il file di configurazione SSL predefinito del sistema default-ssl.conf funzionerà per le nostre esigenze. Tuttavia, se hai acquistato un certificato SSL personalizzato, dovrai modificare il file di configurazione e aggiornare le variabili SSLCertificateFile , SSLCertificateKeyFile e SSLCertificateChainFile per puntare alla posizione in cui hai salvato il certificato e i file chiave (consulta l'autorità di certificazione o il fornitore per ulteriore assistenza nella configurazione).
Ora creeremo un .htaccess file di configurazione che costringerà i visitatori del tuo server web a utilizzare il protocollo HTTPS (SSL).
nano /var/www/html/.htaccess
Copia e incolla le seguenti variabili nel .htaccess configurazione.
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{SERVER_PORT} 80
RewriteRule ^(.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}/$1 [L] Queste variabili di configurazione dicono ad Apache di abilitare il motore mod_rewrite e quindi di reindirizzare i visitatori su HTTP (porta 80) all'URL HTTPS (porta 443).
[Torna su]
5 – Installa e configura Memcached
Memcached è un sistema di memorizzazione nella cache di oggetti a memoria distribuita ad alte prestazioni. Questo pacchetto aiuterà a velocizzare le applicazioni web dinamiche, come RoundCube e Postfix Webadmin.
Per prima cosa, installiamo il pacchetto usando apt-get.
apt-get install memcached
Per i sistemi più piccoli, la configurazione predefinita è generalmente sufficiente. Blocca l'accesso al localhost e fornisce valori di allocazione di memoria sufficienti. Tuttavia, se stai costruendo un server più grande che potrebbe essere utilizzato in modo intenso, molto probabilmente vorrai modificare i valori di allocazione della memoria in modo che siano superiori al valore predefinito di 64 M.
I file di configurazione memcached si trovano in /etc/memcached.conf .
[Torna su]
6 – Installa i pacchetti del server di posta
Ora siamo pronti per installare i pacchetti del server di posta. Anche in questo caso, si trovano in un tasksel gruppo di pacchetti.
apt-get install mail-server^
Per visualizzare un elenco dei pacchetti inclusi in questa installazione di gruppo, puoi eseguire quanto segue:
tasksel --task-packages mail-server
Durante l'installazione del pacchetto, Postfix ti porrà una serie di domande:
- Tipo di configurazione dell'installazione:
Seleziona "Sito Internet ” come tipo di configurazione. - Nome host del server di posta:
Assicurati di inserire lo stesso nome host (FQDN) utilizzato nel passaggio n. 1 - Crea un certificato SSL autofirmato —
Seleziona l'opzione "Sì" - Imposta il nome comune del certificato SSL:
Inserisci lo stesso nome host (FQDN) utilizzato nel passaggio 1
Ora installeremo il resto dei pacchetti necessari al server di posta per supportare gli utenti basati su MySQL, nonché i pacchetti di rilevamento dello spam e dell'antivirus. (Nota:questi pacchetti possono essere installati tramite un singolo apt-get install comando, con ogni nome di pacchetto separato da uno spazio, ma sono presentati qui come comandi separati per facilitarne la lettura.)
apt-get install postfix-mysql dovecot-mysql dovecot-imapd postgrey apt-get install amavis clamav clamav-daemon spamassassin apt-get install php-imap
Il prossimo set di pacchetti opzionali estende le capacità dei pacchetti di rilevamento antispam e antivirus consentendo una maggiore ispezione dei file allegati che arrivano nel tuo server di posta.
apt-get install libnet-dns-perl pyzor razor apt-get install arj bzip2 cabextract cpio file gzip nomarch pax unzip zip
Ora, riavviamo i servizi Apache2 in modo che veda i nuovi moduli che gli abbiamo fornito.
systemctl restart apache2
[Torna su]
7 – Creazione di un database MySQL per il server di posta elettronica
Ora siamo pronti per creare il database per i nostri account utente e altre funzioni del server di posta.
Per iniziare, dobbiamo accedere al servizio di database MySQL come utente root. Avrai bisogno della password che hai inserito per la prima volta nel passaggio n. 2.
mysql -u root -p
Ora vedrai un diverso prompt della riga di comando (mysql> ). Questa è la console della CLI MySQL in cui puoi gestire i database e le tabelle del tuo server MySQL.
Innanzitutto, creeremo un nuovo database chiamato "mail", quindi creeremo un account utente di sistema con autorizzazioni complete per questo nuovo database. Assicurati di sostituire il <secure password> variabile con un'altra *nuova* password sicura per questo account. Non utilizzare la stessa password utilizzata per l'account utente root .
CREATE DATABASE mail; CREATE USER 'mail'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON mail.* TO 'mail'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Ora abbiamo impostato il database che verrà utilizzato dai servizi del tuo server di posta.
[Torna su]
8.1 – Installazione di Postfix Admin
Postfix Admin è uno strumento di gestione basato sul Web creato per Postfix. È un'applicazione basata su PHP che gestisce domini virtuali e utenti in stile Postfix archiviati in MySQL o PostgreSQL.
Innanzitutto, dobbiamo scaricare l'ultima versione dell'applicazione. Questo esempio scaricherà la versione 2.92–controlla sempre la versione sul sito Web del provider per assicurarti di ricevere l'ultima versione .
wget https://excellmedia.dl.sourceforge.net/project/postfixadmin/postfixadmin-3.3.1/PostfixAdmin%203.3.1.tar.gz
Ora estrarremo l'applicazione e la copieremo nella directory HTML /var/www/html/postfixadmin sul nostro server.
tar -xvf PostfixAdmin%203.3.1.tar.gz mv postfixadmin-postfixadmin-cc23eba /var/www/html/postfixadmin
Ora dobbiamo creare una directory di modelli e aggiornare i permessi di questa nuova cartella in modo che i www-data l'account utente vi ha accesso.
mkdir /var/www/html/postfixadmin/templates_c chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/postfixadmin
[Torna su]
8.2 – Configurazione dell'amministratore Postfix
Ora abbiamo alcune configurazioni da aggiornare nei file Postfix Admin. Per prima cosa, modificheremo il config.inc.php file in modo che sappia come comunicare con il database che abbiamo appena creato nel passaggio n. 7.
nano /var/www/html/postfixadmin/config.inc.php
Cerca la variabile 'configured' e reimposta il valore da false su true .
$CONF['configured'] = true;
Ora cerca la variabile 'database_' e sostituisci i valori per la configurazione del tuo server MySQL. Assicurati di sostituire la variabile mypassword con la password per l'utente del database "mail" immessa nel passaggio n. 7.
$CONF['database_type'] = 'mysqli'; $CONF['database_host'] = 'localhost'; $CONF['database_user'] = 'mail'; $CONF['database_password'] = 'mypassword'; $CONF['database_name'] = 'mail';
Ora cerca la variabile 'admin_email' e sostituisci il valore con l'indirizzo email che imposterai per il tuo account email amministratore.
$CONF['admin_email'] = 'example@unixlinux.online';
Ora cerca la variabile 'domain_path' e sostituisci il valore da "YES da ‘ a ‘NO '.
$CONF['domain_path'] = 'NO';
Ora cerca la variabile 'domain_in_mailbox' e sostituire il valore da "NO ‘ a ‘YES '.
$CONF['domain_in_mailbox'] = 'YES';
Queste ultime variabili di configurazione non definiscono il percorso in cui verranno archiviati sul server i dati della casella di posta dell'utente effettivo. Questi verranno definiti in seguito durante le fasi di configurazione di Dovecot.
Ora sei pronto per salvare il file di configurazione, ma non uscire ancora!
Ora apriamo un browser web, inserisci l'URL del tuo server di posta, puntando direttamente al setup.php pagina di configurazione. Assicurati di sostituire mail.example.tld con il nome host del tuo server reale.
https://email.linuxbuz.com/postfixadmin/public/setup.php
Quando accedi all'URL, lo script verificherà automaticamente il server e confermerà che tutti i moduli prerequisiti siano installati e funzionanti.
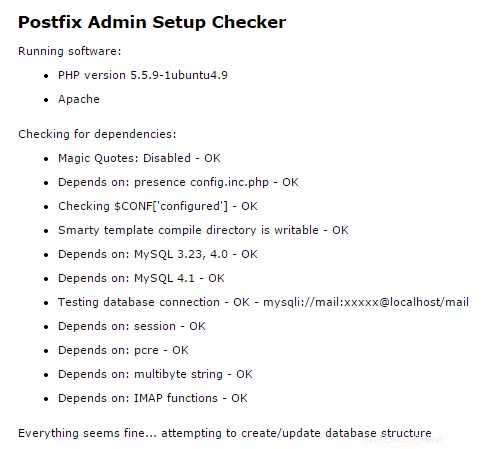
Output del controllo di configurazione dell'amministratore di Postfix
Una volta completati i controlli, ti verrà richiesto di inserire una password di configurazione. Questa password viene utilizzata per creare account di amministratore principale per l'interfaccia web di Postfix Admin.
Inserisci una password sicura e premi il pulsante "Genera hash password".
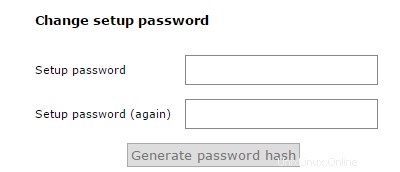
L'amministratore di Postfix genera l'hash della password

Esempio di hash della password di amministratore Postfix
NON chiudere ancora il browser web! Torniamo qui tra pochi minuti.
Dopo aver generato l'hash della password, dovremo quindi aggiornare il config.inc.php file di nuovo con questa password. Cerca la variabile 'setup_password' e sostituisci il valore con quello generato dallo script.
// In order to setup Postfixadmin, you MUST specify a hashed password here. // To create the hash, visit setup.php in a browser and type a password into the field, // on submission it will be echoed out to you as a hashed value. $CONF['setup_password'] = '<enter your hashed password here>';
Ora puoi salvare ed uscire dal file di configurazione.
Ora siamo pronti per tornare al browser web e generare l'account "super amministratore" per il portale di amministrazione di Postfix.
Quando hai fatto clic sul pulsante "Genera hash password", i campi del modulo sono cambiati per assomigliare all'esempio seguente. Ora puoi compilare il modulo per generare un account super amministratore.
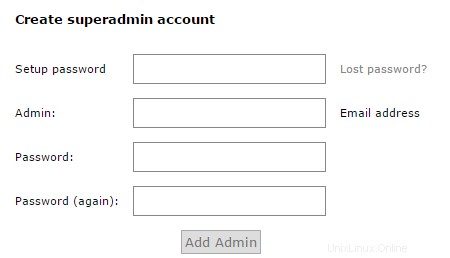
Creazione di un account superadmin con Postfix Admin
Puoi anche creare un utente amministratore con il seguente comando:
bash /var/www/html/postfixadmin/scripts/postfixadmin-cli admin add example@unixlinux.online --superadmin 1 --active 1 --password example@unixlinux.online --password2 example@unixlinux.online
Dovresti ottenere il seguente output:
Welcome to Postfixadmin-CLI v0.3 --------------------------------------------------------------- The admin example@unixlinux.online has been added! ---------------------------------------------------------------
[Torna su]
9 – Aggiunta di account utente (caselle di posta) all'amministratore di Postfix
Ora siamo pronti per creare un account utente virtuale sul nostro server di posta. Per fare ciò, torneremo all'URL di amministrazione di Postfix nel nostro browser web e inseriremo l'URL del tuo server di posta. Assicurati di sostituire mail.example.tld con il nome host del tuo server reale.
https://email.linuxbuz.com/postfixadmin/public
Ora sarai in grado di accedere al portale di amministrazione di Postfix dove puoi gestire domini virtuali e account utente virtuali. Inserisci il nome utente e la password del super amministratore che hai creato sopra durante la configurazione di Postfix Admin, quindi premi il pulsante "Accedi".
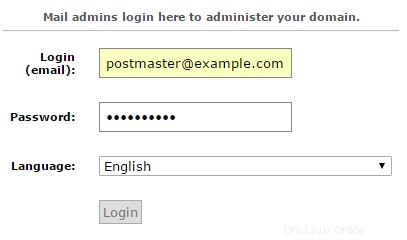
Accesso amministratore per Postfix Admin
Dopo aver effettuato l'accesso al portale di amministrazione di Postfix, vedrai un menu nella parte superiore della pagina.
Le opzioni di menu offrono la possibilità di gestire i domini e gli utenti virtuali del server di posta Postfix e di visualizzare i file di registro.
Menu di amministrazione di Postfix
Amministratore Postfix Aggiungi opzione casella di posta
Per creare una casella di posta utente, fare clic sul collegamento rapido "Aggiungi casella di posta". Verrai ora indirizzato alla schermata "Aggiungi guidata casella di posta". Compila i dettagli nel modulo e premi il pulsante "Aggiungi casella di posta" una volta completato. La procedura guidata creerà il tuo primo account utente virtuale (casella di posta).
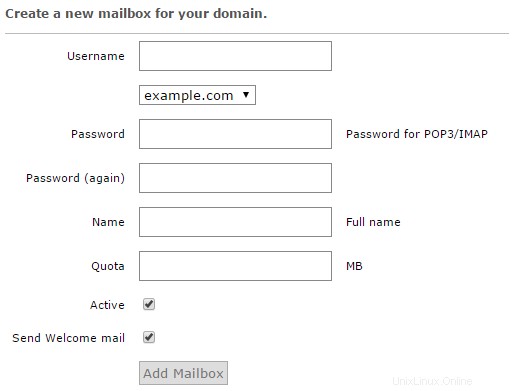
Creazione di una nuova casella di posta in Postfix Admin
[Torna su]
10 – Creare un utente di sistema per gestire le directory di posta virtuali
Gli utenti virtuali sono quelli che tecnicamente non esistono sul tuo server Linux e non utilizzano i metodi Linux standard per l'autenticazione o la consegna e l'archiviazione della posta. Gli account utente virtuali del tuo server di posta sono definiti all'interno del database creato da Postfix Admin piuttosto che esistenti come account utente di sistema, quindi dobbiamo creare un unico account utente di sistema che gestirà servizi come l'archiviazione della posta e l'autenticazione di Dovecot.
Innanzitutto, creiamo un account utente di sistema chiamato vmail e dargli i permessi per le directory richieste. Questo account di sistema sarà responsabile delle operazioni di back-end per l'archiviazione e i servizi delle cassette postali.
useradd -r -u 150 -g mail -d /var/vmail -s /sbin/nologin -c "Virtual MailDir Handler" vmail mkdir -p /var/vmail chown vmail:mail /var/vmail chmod 770 /var/vmail
Una spiegazione dei comandi precedenti:
- Abbiamo creato l'account utente di sistema
vmail, assegnato alla home directory come/var/vmaile limitato la possibilità per questo account di accedere tramite shell o console. - Abbiamo quindi creato manualmente la directory home
/var/vmailper il nuovo account utente di sistema. - Quindi impostiamo il proprietario e il gruppo per
/var/vmaildirectory. - Abbiamo quindi concesso i permessi completi all'utente di sistema
vmaile il gruppo di sicurezzamailassegnato alla directory/var/vmail.
[Torna su]
11 – Configurazione di Dovecot
Dovecot è un server di posta elettronica IMAP e POP3 open source scritto pensando alla sicurezza. Dovecot ha molte funzionalità integrate, che puoi visualizzare sul loro sito Web pubblico, http://www.dovecot.org.
Dovecot sarà responsabile della gestione delle connessioni IMAP e POP3, della gestione delle directory di posta locali e della ricezione della posta in arrivo consegnata dal processo del server di posta SMTP di Postfix. Dovecot gestirà anche l'autenticazione per le connessioni SMTP. Molti file diversi all'interno di /etc/dovecot gestione directory configurazione Dovecot.
Per prima cosa, configuriamo Dovecot per utilizzare il database impostato da Postfix Admin. Per prima cosa modificheremo il file di configurazione /etc/dovecot/conf.d/auth-sql.conf.ext
nano /etc/dovecot/conf.d/auth-sql.conf.ext
Modifica o aggiorna i contenuti per avere la seguente configurazione.
# Look up user passwords from a SQL database as
# defined in /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext
passdb {
driver = sql
args = /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext
}
# Look up user information from a SQL database as
# defined in /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext
userdb {
driver = sql
args = /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext
} Al termine, salva ed esci dal file di configurazione.
File di configurazione SQL
Ora eseguiremo il backup del file di configurazione SQL originale /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext e creare un nuovo file di configurazione da utilizzare per Dovecot.
mv /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext.original nano /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext
Ora copia il contenuto seguente nel file di configurazione e aggiorna i valori per il database di posta che hai impostato nel passaggio 7.
# Database driver: mysql, pgsql, sqlite
driver = mysql
# Database Connection:
# connect = host=192.168.1.1 dbname=users
# connect = host=sql.example.com dbname=virtual user=virtual password=blarg
# connect = /etc/dovecot/authdb.sqlite
#
connect = host=localhost dbname=mail user=mail password=mypassword
# Default password scheme.
#
# List of supported schemes is in
# http://wiki2.dovecot.org/Authentication/PasswordSchemes
#
# Weak but common encryption scheme:
default_pass_scheme = MD5-CRYPT
#
# Comment the above out and uncomment below
# for stronger encryption:
#default_pass_scheme - SHA256-CRYPT
# Define the query to obtain a user password.
password_query = \
SELECT username as user, password, '/var/vmail/%d/%n' as userdb_home, \
'maildir:/var/vmail/%d/%n' as userdb_mail, 150 as userdb_uid, 8 as userdb_gid \
FROM mailbox WHERE username = '%u' AND active = '1'
# Define the query to obtain user information.
user_query = \
SELECT '/var/vmail/%d/%n' as home, 'maildir:/var/vmail/%d/%n' as mail, \
150 AS uid, 8 AS gid, concat('dirsize:storage=', quota) AS quota \
FROM mailbox WHERE username = '%u' AND active = '1' Al termine, salva ed esci da questo file di configurazione.
File di definizione dell'autenticazione
Ora eseguiremo il backup del file di definizione dell'autenticazione /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf e creane uno nuovo.
mv /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf.original nano /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf
Ora copia il contenuto seguente nel file di definizione.
# Disable LOGIN command and all other plaintext authentications unless # SSL/TLS is used (LOGINDISABLED capability). Note that if the remote IP # matches the local IP (ie. you're connecting from the same computer), the # connection is considered secure and plaintext authentication is allowed. disable_plaintext_auth = yes # Space separated list of wanted authentication mechanisms: # plain login digest-md5 cram-md5 ntlm rpa apop anonymous gssapi otp skey # gss-spnego # NOTE: See also disable_plaintext_auth setting. auth_mechanisms = plain login ## ## Password and user databases ## # # Password database is used to verify user's password (and nothing more). # You can have multiple passdbs and userdbs. This is useful if you want to # allow both system users (/etc/passwd) and virtual users to login without # duplicating the system users into virtual database. # # <doc/wiki/PasswordDatabase.txt> # # User database specifies where mails are located and what user/group IDs # own them. For single-UID configuration use "static" userdb. # # <doc/wiki/UserDatabase.txt> # Use the SQL database configuration rather than any of the others. !include auth-sql.conf.ext
Al termine, salva ed esci dal file.
File di definizione della posta
Successivamente, diremo a Dovecot dove archiviare la posta degli utenti virtuali. Eseguiremo il backup del file di definizione della posta /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf e creandone uno nuovo.
mv /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf.original nano /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf
Ora copia il contenuto seguente nel file di definizione.
# Location for users' mailboxes. The default is empty, which means that Dovecot
# tries to find the mailboxes automatically. This won't work if the user
# doesn't yet have any mail, so you should explicitly tell Dovecot the full
# location.
#
# If you're using mbox, giving a path to the INBOX file (eg. /var/mail/%u)
# isn't enough. You'll also need to tell Dovecot where the other mailboxes are
# kept. This is called the "root mail directory", and it must be the first
# path given in the mail_location setting.
#
# There are a few special variables you can use, eg.:
#
# %u - username
# %n - user part in example@unixlinux.online, same as %u if there's no domain
# %d - domain part in example@unixlinux.online, empty if there's no domain
# %h - home directory
#
# See doc/wiki/Variables.txt for full list. Some examples:
#
# mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
# mail_location = mbox:~/mail:INBOX=/var/mail/%u
# mail_location = mbox:/var/mail/%d/%1n/%n:INDEX=/var/indexes/%d/%1n/%n
#
# <doc/wiki/MailLocation.txt>
#
mail_location = maildir:/var/vmail/%d/%n
# System user and group used to access mails. If you use multiple, userdb
# can override these by returning uid or gid fields. You can use either numbers
# or names. <doc/wiki/UserIds.txt>
mail_uid = vmail
mail_gid = mail
# Valid UID range for users, defaults to 500 and above. This is mostly
# to make sure that users can't log in as daemons or other system users.
# Note that denying root logins is hardcoded to dovecot binary and can't
# be done even if first_valid_uid is set to 0.
#
# Use the vmail user uid here.
first_valid_uid = 150
last_valid_uid = 150
# If you need to set multiple mailbox locations or want to change default
# namespace settings, you can do it by defining namespace sections.
#
# You can have private, shared and public namespaces. Private namespaces
# are for user's personal mails. Shared namespaces are for accessing other
# users' mailboxes that have been shared. Public namespaces are for shared
# mailboxes that are managed by sysadmin. If you create any shared or public
# namespaces you'll typically want to enable ACL plugin also, otherwise all
# users can access all the shared mailboxes, assuming they have permissions
# on filesystem level to do so.
namespace inbox {
# Namespace type: private, shared or public
#type = private
# Hierarchy separator to use. You should use the same separator for all
# namespaces or some clients get confused. '/' is usually a good one.
# The default however depends on the underlying mail storage format.
#separator =
# Prefix required to access this namespace. This needs to be different for
# all namespaces. For example "Public/".
#prefix =
# Physical location of the mailbox. This is in same format as
# mail_location, which is also the default for it.
#location =
# There can be only one INBOX, and this setting defines which namespace
# has it.
inbox = yes
# If namespace is hidden, it's not advertised to clients via NAMESPACE
# extension. You'll most likely also want to set list=no. This is mostly
# useful when converting from another server with different namespaces which
# you want to deprecate but still keep working. For example you can create
# hidden namespaces with prefixes "~/mail/", "~%u/mail/" and "mail/".
#hidden = no
# Show the mailboxes under this namespace with LIST command. This makes the
# namespace visible for clients that don't support NAMESPACE extension.
# "children" value lists child mailboxes, but hides the namespace prefix.
#list = yes
# Namespace handles its own subscriptions. If set to "no", the parent
# namespace handles them (empty prefix should always have this as "yes")
#subscriptions = yes
}
Al termine, salva ed esci dal file.
SSL Definition File
If you have an SSL certificate that you would like to install, you will need to modify the Dovecot SSL definition file /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf with your valid certificate. Remember, you will have to also include your CA certificate bundle if one has been provided by the certificate issuer.
Dovecot Master Definition File
We are now going to update the Dovecot master definition file /etc/dovecot/10-master.conf to include the system user account and the postfix settings.
nano /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf
Search for the config definition service auth and replace the definition block with the following.
service auth {
# auth_socket_path points to this userdb socket by default. It's typically
# used by dovecot-lda, doveadm, possibly imap process, etc. Users that have
# full permissions to this socket are able to get a list of all usernames and
# get the results of everyone's userdb lookups.
#
# The default 0666 mode allows anyone to connect to the socket, but the
# userdb lookups will succeed only if the userdb returns an "uid" field that
# matches the caller process's UID. Also if caller's uid or gid matches the
# socket's uid or gid the lookup succeeds. Anything else causes a failure.
#
# To give the caller full permissions to lookup all users, set the mode to
# something else than 0666 and Dovecot lets the kernel enforce the
# permissions (e.g. 0777 allows everyone full permissions).
unix_listener auth-userdb {
mode = 0600
user = vmail
group = mail
}
# Postfix smtp-auth
unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/auth {
mode = 0660
# Assuming the default Postfix userid and groupid
user = postfix
group = postfix
}
} Al termine, salva ed esci dal file.
LDA Definition File
In some cases, you may have to explicitly define the postmaster email address for your server. To do this, you will need to edit the LDA definition file /etc/dovecot/conf.d/15-lda.conf . If you see error messages like Invalid settings: postmaster_address setting not given showing up in the mail server logs, then this configuration change is the likely fix for that error.
nano /etc/dovecot/conf.d/15-lda.conf
Search for the definition postmaster_address and update the value to include your domain’s postmaster account.
# Address to use when sending rejection mails. # Default is example@unixlinux.online<your domain>. %d expands to recipient domain. #postmaster_address = postmaster_address = example@unixlinux.online
Al termine, salva ed esci dal file.
We now need to update the Dovecot configuration directory to be accessible to the Dovecot service account as well as the vmail system account.
chown -R vmail:dovecot /etc/dovecot chmod -R o-rwx /etc/dovecot
You have now completed the configuration of the Dovecot service and we can now move on to the antivirus and anti-spam services.
[Back to top]
12 – Configuring Amavis, ClamAV, and SpamAssassin
What are these packages?
– Amavis is an interface between Postfix and content filtering packages such as SpamAssassin and ClamAV.
– ClamAV is a high-performance antivirus engine for detecting trojans, viruses, malware &other malicious threats.
– SpamAssassin is a high-performance anti-spam platform famous for its Bayesian spam filtering capabilities. It gives system administrators a filter to classify messages and block unsolicited bulk email.
We will now walk you through the process of installing some protection for your mail server. For the most part, the default configurations are sufficient for a good line of defense against spam and viruses getting through your mail server. If you have special requirements, you can, of course, spend a good amount of time crafting intricate processing rules.
Let’s first create the two system user accounts, amavis and clamav, and allow them to collaborate together.
adduser clamav amavis adduser amavis clamav
We are now going to enable the Amavis daemon by editing the /etc/amavis/conf.d/15-content_filter_mode file di configurazione.
nano /etc/amavis/conf.d/15-content_filter_mode
use strict; # You can modify this file to re-enable SPAM checking through spamassassin # and to re-enable antivirus checking. # # Default antivirus checking mode # Please note, that anti-virus checking is DISABLED by # default. # If You wish to enable it, please uncomment the following lines: @bypass_virus_checks_maps = ( %bypass_virus_checks, @bypass_virus_checks_acl, $bypass_virus_checks_re); # # Default SPAM checking mode # Please note, that anti-spam checking is DISABLED by # default. # If You wish to enable it, please uncomment the following lines: @bypass_spam_checks_maps = ( %bypass_spam_checks, @bypass_spam_checks_acl, $bypass_spam_checks_re); 1; # ensure a defined return
Once done, you can save and exit the file.
We are now going to enable the SpamAssassin software by editing the /etc/default/spamassassin file di configurazione.
nano /etc/default/spamassassin
Now search for the variable CRON=0 in the configuration file and change the value to 1.
# Cronjob # Set to anything but 0 to enable the cron job to automatically update # spamassassin's rules on a nightly basis CRON=1
Next, enable the SpamAssassin software with the following command:
update-rc.d spamassassin enable
We are now going to set up Amavis to use the database from Postfix Admin to identify mail that is arriving for local delivery. By default, SpamAssassin and Amavis will only check mail that is determined to be arriving for local delivery. Because we are set up to use virtual user mailboxes, we have to tell the services where to locate the user accounts.
To do this, we need to update the configuration file /etc/amavis/conf.d/50-user .
nano /etc/amavis/conf.d/50-user
Replace the contents of this configuration file with the below. Be sure to update the MySQL database password to use the password for the database user “mail” that you entered in Step #7.
use strict;
#
# Place your configuration directives here. They will override those in
# earlier files.
#
# See /usr/share/doc/amavisd-new/ for documentation and examples of
# the directives you can use in this file
#
# Three concurrent processes. This should fit into the RAM available on an
# AWS micro instance. This has to match the number of processes specified
# for Amavis in /etc/postfix/master.cf.
$max_servers = 3;
# Add spam info headers if at or above that level - this ensures they
# are always added.
$sa_tag_level_deflt = -9999;
# Check the database to see if mail is for local delivery, and thus
# should be spam checked.
@lookup_sql_dsn = (
['DBI:mysql:database=mail;host=127.0.0.1;port=3306',
'mail',
'mypassword']);
$sql_select_policy = 'SELECT domain from domain WHERE CONCAT("@",domain) IN (%k)';
# Uncomment to bump up the log level when testing.
# $log_level = 2;
#------------ Do not modify anything below this line -------------
1; # ensure a defined return Once done, save and exit the configuration file.
We will now need to restart the Amavis and SpamAssassin services so that they see the new configuration settings.
service amavis restart services spamassassin restart
[Back to top]
13 – Configuring Postfix
We are now ready to configure the Postfix mail server. Postfix handles all of the incoming and outgoing mail via the SMTP protocol, and we are going to configure it to integrate will all of the other software packages that we have just configured.
From a high level view, we are needing Postfix to hand off incoming mail to the SpamAssassin and ClamAV scanners for filtering, and then to pass unblocked mail messages on to the Dovecot services for final mailbox delivery. Postfix will also authenticate the virtual users who connect via SMTP in order to send email messages.
We are going to create a definition file for Postfix to identify users and mailboxes. Please note that the “hosts” directive in these configuration files must be exactly the same as the “bind-address” in the /etc/mysql/my.cnf configuration files.
First, let’s look up the value of the bind-address in the MySQL configuration files.
cat /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf | grep bind-address
<< output >> bind-address = 127.0.0.1
Now that we have the configuration value, we are going to create the required Postfix definition files.
Copy and paste the content for each file. Make sure to update the password value with the password for the database user “mail” that you entered in Step #7.
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_domainaliases_maps.cf
nano /etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_domainaliases_maps.cf
user = mail
password = mypassword
hosts = 127.0.0.1
dbname = mail
query = SELECT goto FROM alias,alias_domain WHERE alias_domain.alias_domain = '%d' AND alias.address=concat('%u', '@', alias_domain.target_domain) AND alias.active = 1 Once done, save and exit the configuration file.
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_maps.cf
nano /etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_maps.cf
user = mail password = mypassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail table = alias select_field = goto where_field = address additional_conditions = and active = '1'
Once done, save and exit the configuration file.
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_domains_maps.cf
nano /etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_domains_maps.cf
user = mail password = mypassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail table = domain select_field = domain where_field = domain additional_conditions = and backupmx = '0' and active = '1'
Once done, save and exit the configuration file.
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_domainaliases_maps.cf
nano /etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_domainaliases_maps.cf
user = mail
password = mypassword
hosts = 127.0.0.1
dbname = mail
query = SELECT maildir FROM mailbox, alias_domain
WHERE alias_domain.alias_domain = '%d'
AND mailbox.username=concat('%u', '@', alias_domain.target_domain )
AND mailbox.active = 1 Once done, save and exit the configuration file.
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_maps.cf
nano /etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_maps.cf
user = mail password = mypassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail table = mailbox select_field = CONCAT(domain, '/', local_part) where_field = username additional_conditions = and active = '1'
Once done, save and exit the configuration file.
We are now going to create the Postfix header-checking directives. These directives remove certain headers when relaying mail through the system. This helps improve privacy for sending users by removing specific headers like origin IP Address and the mail software identifiers. Copy and paste the below content into the file.
nano /etc/postfix/header_checks
/^Received:/ IGNORE /^User-Agent:/ IGNORE /^X-Mailer:/ IGNORE /^X-Originating-IP:/ IGNORE /^x-cr-[a-z]*:/ IGNORE /^Thread-Index:/ IGNORE
Once done, save and exit.
We are now ready to make some changes to the system default Postfix /etc/postfix/main.cf file di configurazione.
This file contains a large amount of complex choices and options for a Postfix server installation. It is far beyond the scope of this article to explain every option or best practice available, so we strongly suggest that you read through the Postfix configuration options /usr/share/postfix/main.cf.dist or the software vendor online manual. O’Reilly has also published a very good book named Postfix:The Definitive Guide .
First, we are going to create a backup of the original main.cf configuration file and then create a new copy of the file.
mv /etc/postfix/main.cf /etc/postfix/main.cf.original nano /etc/postfix/main.cf
Now, copy the below content into the /etc/postfix/main.cf file di configurazione.
# See /usr/share/postfix/main.cf.dist for a commented, more complete version
# The first text sent to a connecting process.
smtpd_banner = $myhostname ESMTP $mail_name
biff = no
# appending .domain is the MUA's job.
append_dot_mydomain = no
readme_directory = no
# SASL parameters
# ---------------------------------
# Use Dovecot to authenticate.
smtpd_sasl_type = dovecot
# Referring to /var/spool/postfix/private/auth
smtpd_sasl_path = private/auth
smtpd_sasl_auth_enable = yes
broken_sasl_auth_clients = yes
smtpd_sasl_security_options = noanonymous
smtpd_sasl_local_domain =
smtpd_sasl_authenticated_header = yes
# TLS parameters
# ---------------------------------
# Replace this with your SSL certificate path if you are using one.
smtpd_tls_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
smtpd_tls_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# The snakeoil self-signed certificate has no need for a CA file. But
# if you are using your own SSL certificate, then you probably have
# a CA certificate bundle from your provider. The path to that goes
# here.
#smtpd_tls_CAfile=/path/to/ca/file
smtp_tls_note_starttls_offer = yes
smtpd_tls_loglevel = 1
smtpd_tls_received_header = yes
smtpd_tls_session_cache_timeout = 3600s
tls_random_source = dev:/dev/urandom
#smtpd_tls_session_cache_database = btree:${data_directory}/smtpd_scache
#smtp_tls_session_cache_database = btree:${data_directory}/smtp_scache
# Note that forcing use of TLS is going to cause breakage - most mail servers
# don't offer it and so delivery will fail, both incoming and outgoing. This is
# unfortunate given what various governmental agencies are up to these days.
# These are Postfix 2.2 only.
#
# Enable (but don't force) use of TLS on incoming smtp connections.
smtpd_use_tls = yes
smtpd_enforce_tls = no
# Enable (but don't force) use of TLS on outgoing smtp connections.
smtp_use_tls = yes
smtp_enforce_tls = no
# These are Postfix 2.3 and later.
#
# Enable (but don't force) all incoming smtp connections to use TLS.
smtpd_tls_security_level = may
# Enable (but don't force) all outgoing smtp connections to use TLS.
smtp_tls_security_level = may
# See /usr/share/doc/postfix/TLS_README.gz in the postfix-doc package for
# information on enabling SSL in the smtp client.
# SMTPD parameters
# ---------------------------------
# Uncomment the next line to generate "delayed mail" warnings
#delay_warning_time = 4h
# will it be a permanent error or temporary
unknown_local_recipient_reject_code = 450
# how long to keep message on queue before return as failed.
# some have 3 days, I have 16 days as I am backup server for some people
# whom go on holiday with their server switched off.
maximal_queue_lifetime = 7d
# max and min time in seconds between retries if connection failed
minimal_backoff_time = 1000s
maximal_backoff_time = 8000s
# how long to wait when servers connect before receiving rest of data
smtp_helo_timeout = 60s
# how many address can be used in one message.
# effective stopper to mass spammers, accidental copy in whole address list
# but may restrict intentional mail shots.
smtpd_recipient_limit = 16
# how many error before back off.
smtpd_soft_error_limit = 3
# how many max errors before blocking it.
smtpd_hard_error_limit = 12
# This next set are important for determining who can send mail and relay mail
# to other servers. It is very important to get this right - accidentally producing
# an open relay that allows unauthenticated sending of mail is a Very Bad Thing.
#
# You are encouraged to read up on what exactly each of these options accomplish.
# Requirements for the HELO statement
smtpd_helo_restrictions = permit_mynetworks, warn_if_reject reject_non_fqdn_hostname, reject_invalid_hostname, permit
# Requirements for the sender details
smtpd_sender_restrictions = permit_sasl_authenticated, permit_mynetworks, warn_if_reject reject_non_fqdn_sender, reject_unknown_sender_domain, reject_unauth_pipelining, permit
# Requirements for the connecting server
# This is primarily the RBL (Realtime Blacklist) Filtering
smtpd_client_restrictions = reject_rbl_client b.barracudacentral.org, reject_rbl_client zen.spamhaus.org, reject_rbl_client spam.dnsbl.sorbs.net
# Requirement for the recipient address. Note that the entry for
# "check_policy_service inet:127.0.0.1:10023" enables Postgrey.
smtpd_recipient_restrictions = reject_unauth_pipelining, permit_mynetworks, permit_sasl_authenticated, reject_non_fqdn_recipient, reject_unknown_recipient_domain, reject_unauth_destination, check_policy_service inet:127.0.0.1:10023, permit
smtpd_data_restrictions = reject_unauth_pipelining
# This is a new option as of Postfix 2.10+, and is required in addition to
# smtpd_recipient_restrictions for things to work properly in this setup.
smtpd_relay_restrictions = reject_unauth_pipelining, permit_mynetworks, permit_sasl_authenticated, reject_non_fqdn_recipient, reject_unknown_recipient_domain, reject_unauth_destination, check_policy_service inet:127.0.0.1:10023, permit
# require proper helo at connections
smtpd_helo_required = yes
# waste spammers time before rejecting them
smtpd_delay_reject = yes
disable_vrfy_command = yes
# General host and delivery info
# ----------------------------------
myhostname = email.linuxbuz.com
myorigin = /etc/hostname
# Some people see issues when setting mydestination explicitly to the server
# subdomain, while leaving it empty generally doesn't hurt. So it is left empty here.
# mydestination = mail.example.com, localhost
mydestination =
# If you have a separate web server that sends outgoing mail through this
# mailserver, you may want to add its IP address to the space-delimited list in
# mynetworks, e.g. as 111.222.333.444/32.
mynetworks = 127.0.0.0/8 [::ffff:127.0.0.0]/104 [::1]/128
mailbox_size_limit = 0
recipient_delimiter = +
inet_interfaces = all
mynetworks_style = host
# This specifies where the virtual mailbox folders will be located.
virtual_mailbox_base = /var/vmail
# This is for the mailbox location for each user. The domainaliases
# map allows us to make use of Postfix Admin's domain alias feature.
virtual_mailbox_maps = mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_maps.cf, mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_domainaliases_maps.cf
# and their user id
virtual_uid_maps = static:150
# and group id
virtual_gid_maps = static:8
# This is for aliases. The domainaliases map allows us to make
# use of Postfix Admin's domain alias feature.
virtual_alias_maps = mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_maps.cf, mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_domainaliases_maps.cf
# This is for domain lookups.
virtual_mailbox_domains = mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_domains_maps.cf
# Integration with other packages
# ---------------------------------------
# Tell postfix to hand off mail to the definition for dovecot in master.cf
virtual_transport = dovecot
dovecot_destination_recipient_limit = 1
# Use amavis for virus and spam scanning
content_filter = amavis:[127.0.0.1]:10024
# Header manipulation
# --------------------------------------
# Getting rid of unwanted headers. See: https://posluns.com/guides/header-removal/
header_checks = regexp:/etc/postfix/header_checks
# getting rid of x-original-to
enable_original_recipient = no
Once done, save and exit.
We are now ready to move on to the Postfix /etc/postfix/master.cf file di configurazione. This configuration file also contains a large number of complex choices and options for a Postfix server installation that is far beyond the scope of this article to explain.
We are going to create a backup of the original master.cf configuration file and then create a new file.
mv /etc/postfix/master.cf /etc/postfix/master.cf.original nano /etc/postfix/master.cf
Now, copy the below content into the /etc/postfix/master.cf file di configurazione.
#
# Postfix master process configuration file. For details on the format
# of the file, see the master(5) manual page (command: "man 5 master").
#
# Do not forget to execute "postfix reload" after editing this file.
#
# ==========================================================================
# service type private unpriv chroot wakeup maxproc command + args
# (yes) (yes) (yes) (never) (100)
# ==========================================================================
# SMTP on port 25, unencrypted.
smtp inet n - - - - smtpd
#smtp inet n - - - 1 postscreen
#smtpd pass - - - - - smtpd
#dnsblog unix - - - - 0 dnsblog
#tlsproxy unix - - - - 0 tlsproxy
# SMTP with TLS on port 587.
submission inet n - - - - smtpd
-o syslog_name=postfix/submission
-o smtpd_tls_security_level=encrypt
-o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes
-o smtpd_enforce_tls=yes
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject_unauth_destination,reject
-o smtpd_sasl_tls_security_options=noanonymous
# SMTP over SSL on port 465.
smtps inet n - - - - smtpd
-o syslog_name=postfix/smtps
-o smtpd_tls_wrappermode=yes
-o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes
-o smtpd_tls_auth_only=yes
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject_unauth_destination,reject
-o smtpd_sasl_security_options=noanonymous,noplaintext
-o smtpd_sasl_tls_security_options=noanonymous
#628 inet n - - - - qmqpd
pickup fifo n - - 60 1 pickup
-o content_filter=
-o receive_override_options=no_header_body_checks
cleanup unix n - - - 0 cleanup
qmgr fifo n - n 300 1 qmgr
#qmgr fifo n - n 300 1 oqmgr
tlsmgr unix - - - 1000? 1 tlsmgr
rewrite unix - - - - - trivial-rewrite
bounce unix - - - - 0 bounce
defer unix - - - - 0 bounce
trace unix - - - - 0 bounce
verify unix - - - - 1 verify
flush unix n - - 1000? 0 flush
proxymap unix - - n - - proxymap
proxywrite unix - - n - 1 proxymap
smtp unix - - - - - smtp
relay unix - - - - - smtp
# -o smtp_helo_timeout=5 -o smtp_connect_timeout=5
showq unix n - - - - showq
error unix - - - - - error
retry unix - - - - - error
discard unix - - - - - discard
local unix - n n - - local
virtual unix - n n - - virtual
lmtp unix - - - - - lmtp
anvil unix - - - - 1 anvil
scache unix - - - - 1 scache
#
# ====================================================================
# Interfaces to non-Postfix software. Be sure to examine the manual
# pages of the non-Postfix software to find out what options it wants.
#
# Many of the following services use the Postfix pipe(8) delivery
# agent. See the pipe(8) man page for information about ${recipient}
# and other message envelope options.
# ====================================================================
#
# maildrop. See the Postfix MAILDROP_README file for details.
# Also specify in main.cf: maildrop_destination_recipient_limit=1
#
maildrop unix - n n - - pipe
flags=DRhu user=vmail argv=/usr/bin/maildrop -d ${recipient}
#
# ====================================================================
#
# Recent Cyrus versions can use the existing "lmtp" master.cf entry.
#
# Specify in cyrus.conf:
# lmtp cmd="lmtpd -a" listen="localhost:lmtp" proto=tcp4
#
# Specify in main.cf one or more of the following:
# mailbox_transport = lmtp:inet:localhost
# virtual_transport = lmtp:inet:localhost
#
# ====================================================================
#
# Cyrus 2.1.5 (Amos Gouaux)
# Also specify in main.cf: cyrus_destination_recipient_limit=1
#
#cyrus unix - n n - - pipe
# user=cyrus argv=/cyrus/bin/deliver -e -r ${sender} -m ${extension} ${user}
#
# ====================================================================
# Old example of delivery via Cyrus.
#
#old-cyrus unix - n n - - pipe
# flags=R user=cyrus argv=/cyrus/bin/deliver -e -m ${extension} ${user}
#
# ====================================================================
#
# See the Postfix UUCP_README file for configuration details.
#
uucp unix - n n - - pipe
flags=Fqhu user=uucp argv=uux -r -n -z -a$sender - $nexthop!rmail ($recipient)
#
# Other external delivery methods.
#
ifmail unix - n n - - pipe
flags=F user=ftn argv=/usr/lib/ifmail/ifmail -r $nexthop ($recipient)
bsmtp unix - n n - - pipe
flags=Fq. user=bsmtp argv=/usr/lib/bsmtp/bsmtp -t$nexthop -f$sender $recipient
scalemail-backend unix - n n - 2 pipe
flags=R user=scalemail argv=/usr/lib/scalemail/bin/scalemail-store ${nexthop} ${user} ${extension}
mailman unix - n n - - pipe
flags=FR user=list argv=/usr/lib/mailman/bin/postfix-to-mailman.py
${nexthop} ${user}
# The next two entries integrate with Amavis for anti-virus/spam checks.
amavis unix - - - - 3 smtp
-o smtp_data_done_timeout=1200
-o smtp_send_xforward_command=yes
-o disable_dns_lookups=yes
-o max_use=20
127.0.0.1:10025 inet n - - - - smtpd
-o content_filter=
-o local_recipient_maps=
-o relay_recipient_maps=
-o smtpd_restriction_classes=
-o smtpd_delay_reject=no
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,reject
-o smtpd_helo_restrictions=
-o smtpd_sender_restrictions=
-o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,reject
-o smtpd_data_restrictions=reject_unauth_pipelining
-o smtpd_end_of_data_restrictions=
-o mynetworks=127.0.0.0/8
-o smtpd_error_sleep_time=0
-o smtpd_soft_error_limit=1001
-o smtpd_hard_error_limit=1000
-o smtpd_client_connection_count_limit=0
-o smtpd_client_connection_rate_limit=0
-o receive_override_options=no_header_body_checks,no_unknown_recipient_checks
# Integration with Dovecot - hand mail over to it for local delivery, and
# run the process under the vmail user and mail group.
dovecot unix - n n - - pipe
flags=DRhu user=vmail:mail argv=/usr/lib/dovecot/dovecot-lda -d $(recipient) Once done, save and exit.
We are now ready to restart all of the mail services and test the server.
service postfix restart service spamassassin restart service clamav-daemon restart service amavis restart service dovecot restart
While testing your new mail server, make sure to watch the log files closely for any errors or unusual responses.
The mail server log files are located here:
- General Logging:
/var/log/mail.log - Error Logging:
/var/log/mail.err
[Back to top]
14 – Reverse DNS Lookup
You will now need to set up reverse DNS lookup for your mail server.
Reverse DNS is IP-address-to-domain-name mapping – the opposite of forward (normal) DNS which maps domain names to IP addresses. Reverse DNS is mostly used by people for such things as tracking where a website visitor came from or where an email message originated, for example. Reverse DNS is also important for mail server applications. Many email servers on the Internet are configured to reject incoming emails from any IP address which does not have reverse DNS record configured.
Unless you also administer your own DNS server, you can update reverse DNS with your ISP (Internet Service Provider) or via the hosting provider of your server.
[Back to top]
15 – Install RoundCube Webmail
Now we are going to install the RoundCube Webmail application. This application will allow your remote users to connect to their mailbox through a web browser.
apt-get install roundcube roundcube-mysql roundcube-plugins roundcube-plugins-extra
During the installation process, the system will ask you the prerequisite install questions. Note:you will need the password for the MySQL root user you set up in Step 2.
Configure database for roundcube with dbconfig-common? >> Select 'YES' Database type to be used by roundcube: >> Select 'mysql' Password of the database's administrative user: >> Enter the 'root' MySQL password that you created. MySQL application password for roundcube: >> Enter a new secure password for the RoundCube application to use.
Once you are finished with the pre-installation questions, you should see the following output. Double check the output to make sure there are not errors posted during the installation process.
dbconfig-common: writing config to /etc/dbconfig-common/roundcube.conf Creating config file /etc/dbconfig-common/roundcube.conf with new version Creating config file /etc/roundcube/debian-db.php with new version granting access to database roundcube for example@unixlinux.online: success. verifying access for example@unixlinux.online: success. creating database roundcube: success. verifying database roundcube exists: success. populating database via sql... done. dbconfig-common: flushing administrative password Creating config file /etc/roundcube/config.inc.php with new version apache2_invoke: Enable configuration roundcube.conf * Reloading web server apache2 * * Reloading web server apache2 * Setting up roundcube (1.4.3) ... Setting up roundcube-plugins (1.4.3) ... Setting up roundcube-plugins-extra (0.9.2-20130819) ... Processing triggers for dictionaries-common (1.20.5) ... aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en-common] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en-variant_0] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en-variant_1] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en-variant_2] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en-w_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en-wo_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_CA-variant_0] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_CA-variant_1] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_CA-w_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_CA-wo_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_GB-ise-w_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_GB-ise-wo_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_GB-ize-w_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_GB-ize-wo_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_GB-variant_0] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_GB-variant_1] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_US-w_accents-only] aspell-autobuildhash: processing: en [en_US-wo_accents-only] Setting up aspell (0.60.7~20110707-1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for dictionaries-common (1.20.5) ... Setting up aspell-en (7.1-0-1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.19-0ubuntu6.6) ... Processing triggers for dictionaries-common (1.20.5) ... example@unixlinux.online#
Next, we need to customize some of the RoundCube configuration files. First, we are going to add the RoundCube application into our current Apache configuration files using path alias directives. The default configuration file is installed at /etc/apache2/conf-available/roundcube.conf
nano /etc/apache2/conf-available/roundcube.conf
We now need to remove the two comment flags in front of the alias directives. If you would like to use a different alias name, you can change that here as well. The default alias will use the URL http://<your-server-url>/roundcube/
Alias /roundcube/program/js/tiny_mce/ /usr/share/tinymce/www/
Alias /roundcube /var/lib/roundcube Al termine, salva ed esci dal file.
Now we are going to modify the /etc/roundcube/config.inc.php file di configurazione. This file is where you can customize the RoundCube advanced settings.
nano /etc/roundcube/config.inc.php
Locate the following directives and update the values to match the following.
$config['default_host'] = ''; $config['smtp_server'] = 'localhost'; $config['smtp_port'] = 25; $config['smtp_user'] = '%u'; $config['smtp_pass'] = '%p'; $config['support_url'] = '';
Once done, save and exit the configuration file.
Finally, restart the apache service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart apache2
You should now be able to use your new RoundCube webmail application for sending and receiving message.
[Back to top]
Congratulations!
You have now set up a fully functional and secure mail server on your VPS hosting account from Atlantic.Net.
Scopri di più sui nostri servizi di hosting VPS e sui server privati virtuali.