Questo articolo riguarda il protocollo di tunneling di livello 2 (L2TP) con IPsec per fornire la crittografia end-to-end nella VPN di livello 2 perché le funzionalità di sicurezza non sono disponibili in L2TP. Le implementazioni open source di IPsec sono StrongSwan e OpenSwan, entrambe sono supportate su tutte le distribuzioni Linux. In questo tutorial, OpenSwan viene utilizzato per fornire il canale di sicurezza per L2TP VPN. Freeradius è un noto strumento open source che fornisce diversi tipi di autenticazione per gli utenti. Freeradius viene utilizzato per autenticare l'utente VPN L2TP prima di stabilire un canale sicuro. Un client basato su Android verrà utilizzato per il tunnel sicuro basato su L2TP.
Installazione dei pacchetti richiesti
I seguenti pacchetti importanti verranno installati su Ubuntu 16.04 LTS.
- Server/Client Freeradius
- Server Poptop
- xl2tpd
- Openswan per IPsec
- Server/client MySQL
- Bison &Flex
- Libreria di sviluppo GMP
Come mostrato di seguito, la maggior parte dei pacchetti richiesti sono tutti disponibili nel repository LTS di Ubuntu 16.04.
apt-get update
apt-get install -y mysql-server mysql-client freeradius-mysql pptpd xl2tpd
Lo screenshot seguente mostra come viene impostata la password per l'utente "root" del server di database MySQL durante il processo di installazione.
I seguenti pacchetti sono richiesti per l'installazione di OpenSwan dal sorgente sulla piattaforma Ubuntu 16.04.
apt-get install -y build-essential libgmp3-dev bison flex
Il client Freeradius ei pacchetti OpenSwan non sono disponibili nel repository, quindi entrambi gli strumenti sono stati installati dal sorgente.
Installazione del client Freeradius
Scarica l'ultimo client Freeradius dal seguente link:
wget https://github.com/FreeRADIUS/freeradius-client/archive/master.zip
unzip master.zip
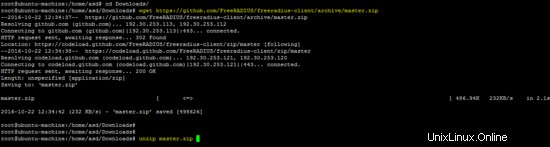
mv freeradius-client-master freeradius-client
cd freeradius-client
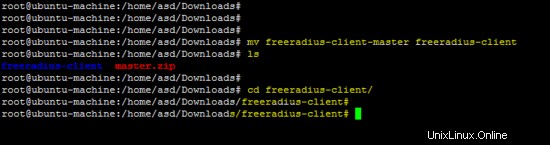
Innanzitutto, esegui lo script configure con l'opzione del prefisso e installa il software utilizzando il comando make.
./configure --prefix=/
make && make install
Installazione di OpenSwan
Il codice sorgente dello strumento OpenSwan IPsec è disponibile al seguente link. Scarica l'archivio e decomprimilo.
wget https://download.openswan.org/openswan/openswan-latest.tar.gz
tar -xzf openswan-latest.tar.gz
cd openswan-*
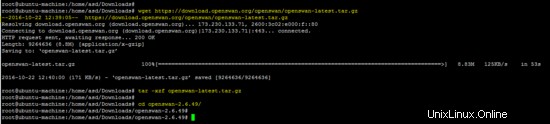
Esegui il comando seguente per compilare e installare OpenSwan.
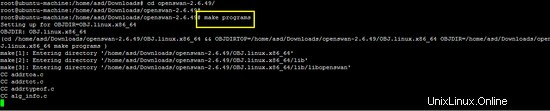
make programs
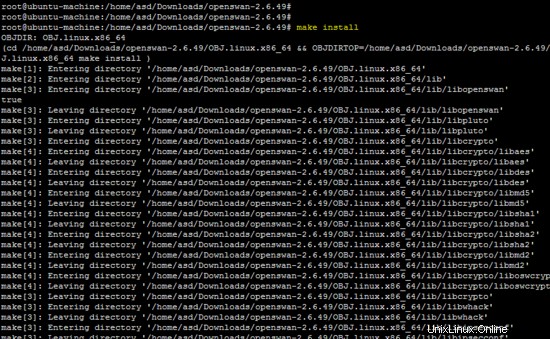
make install
Configurazione
Prima di iniziare con la configurazione dei pacchetti installati, sulla piattaforma Ubuntu sono necessarie le seguenti configurazioni di base (iptables e sysctl).
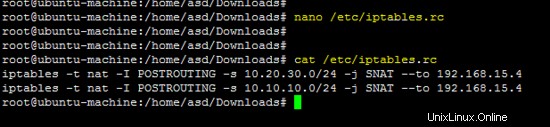
Inserisci le seguenti regole iptables per entrambe le reti (10.20.30.0/24 e 10.10.10.0/24) sul terminale.
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s 10.20.30.0/24 -j SNAT --to 192.168.15.4
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s 10.10.10.0/24 -j SNAT --to 192.168.15.4

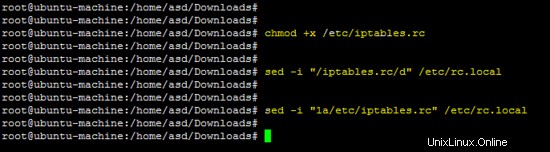
Le regole di cui sopra devono essere salvate in /etc/iptables.rc per applicarli all'avvio.
chmod +x /etc/iptables.rc
sed -i "/iptables.rc/d" /etc/rc.local
sed -i "1a/etc/iptables.rc" /etc/rc.local
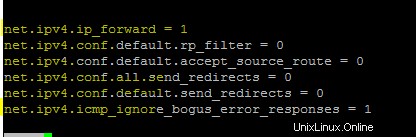
Aggiungi le seguenti righe in /etc/sysctl.conf file per abilitare l'inoltro sulla macchina Linux.
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.icmp_ignore_bogus_error_responses = 1
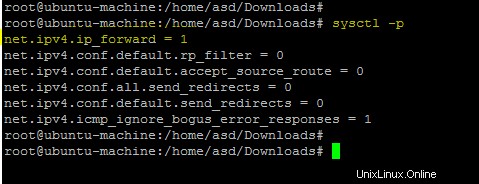
Esegui il comando seguente per applicare le modifiche.
sysctl -p
Configurazione del server Freeradius
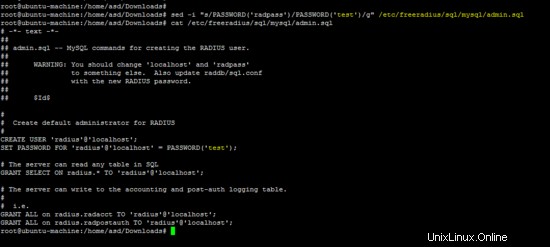
Esegui il comando seguente per modificare la password per freeradius.
sed -i "s/PASSWORD('radpass')/PASSWORD('test')/g" /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/admin.sql
I seguenti comandi MySQL configureranno il server Freeradius su Ubuntu.
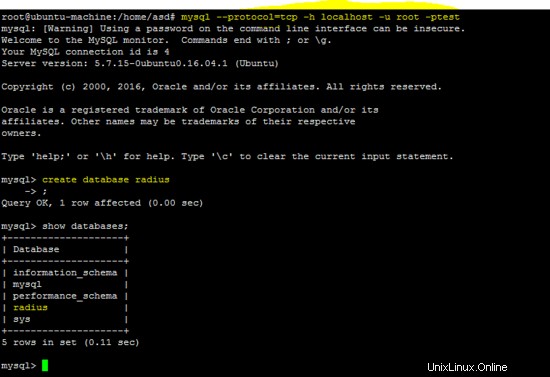
mysql --protocol=tcp -h localhost -u root -ptest
create database radius # create DB radius
mysql --protocol=tcp -h localhost -u root -ptest raggio
mysql --protocol=tcp -h localhost -u root -ptest radius < /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/cui.sql

Aggiunta di una data corretta per risolvere il problema relativo al valore predefinito non valido in /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/cui.sql .
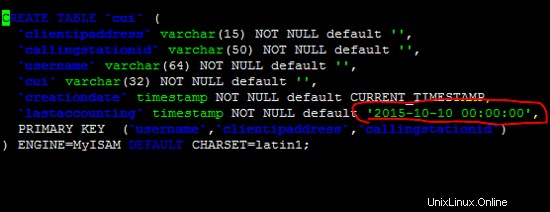
Dopo la correzione in /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/cui.sql file ed esegui nuovamente il comando precedente per correggere l'errore precedente.

mysql --protocol=tcp -h localhost -u root -ptest radius < /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/ippool.sql

mysql --protocol=tcp -h localhost -u root -ptest radius < /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/nas.sql

mysql --protocol=tcp -h localhost -u root -ptest radius < /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/schema.sql

mysql --protocol=tcp -h localhost -u root -ptest radius < /etc/freeradius/sql/mysql/wimax.sql

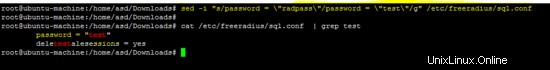
Esegui il seguente comando sed per modificare la password predefinita dell'utente "radius". In questo tutorial, la password per l'utente "raggio" è "test". Scegli una password sicura sul tuo server.
sed -i "s/password = \"radpass\"/password = \"test\"/g" /etc/freeradius/sql.conf

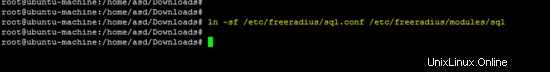
Creazione di un collegamento software per la configurazione sql nella directory dei moduli del server Freeradius.
ln -sf /etc/freeradius/sql.conf /etc/freeradius/modules/sql
I seguenti file non sono presenti su Ubuntu 16.04, quindi creare tutti i file richiesti con il contenuto descritto .
- /etc/freeradius/modules/hourlytraffic
- /etc/freeradius/modules/dailytraffic
- /etc/freeradius/modules/monthlytraffic
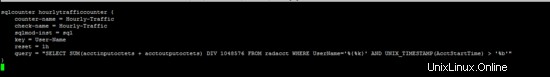
/etc/freeradius/modules/hourlytraffic
sqlcounter hourlytrafficcounter {
counter-name = Hourly-Traffic
check-name = Hourly-Traffic
sqlmod-inst = sql
key = User-Name
reset = 1h
query = "SELECT SUM(acctinputoctets + acctoutputoctets) DIV 1048576 FROM radacct WHERE UserName='%{%k}' AND UNIX_TIMESTAMP(AcctStartTime) > '%b'"
}
/etc/freeradius/modules/dailytraffic
sqlcounter dailytrafficcounter {
counter-name = Daily-Traffic
check-name = Daily-Traffic
sqlmod-inst = sql
key = User-Name
reset = daily
query = "SELECT SUM(acctinputoctets + acctoutputoctets) DIV 1048576 FROM radacct WHERE UserName='%{%k}' AND UNIX_TIMESTAMP(AcctStartTime) > '%b'"
}
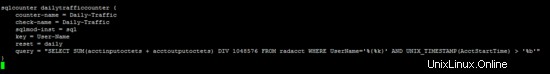
/etc/freeradius/modules/monthlytraffic
sqlcounter monthlytrafficcounter {
counter-name = Monthly-Traffic
check-name = Monthly-Traffic
sqlmod-inst = sql
key = User-Name
reset = monthly
query = "SELECT SUM(acctinputoctets + acctoutputoctets) DIV 1048576 FROM radacct WHERE UserName='%{%k}' AND UNIX_TIMESTAMP(AcctStartTime) > '%b'"
}

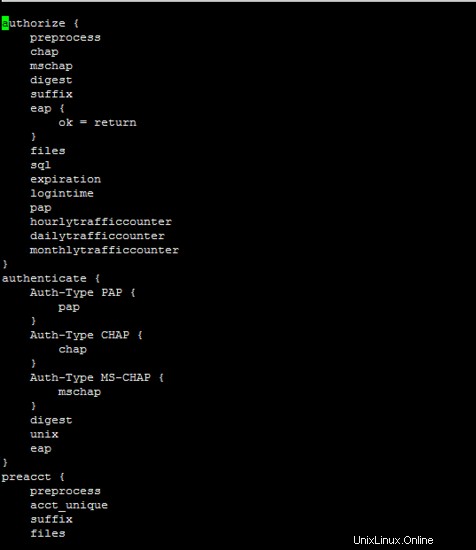
Il seguente file è importante per la configurazione del server freeradius. Le nostre configurazioni in esecuzione sono riportate di seguito.
/etc/freeradius/sites-enabled/default
authorize {
preprocess
chap
mschap
digest
suffix
eap {
ok = return
}
files
sql
expiration
logintime
pap
hourlytrafficcounter
dailytrafficcounter
monthlytrafficcounter
}
authenticate {
Auth-Type PAP {
pap
}
Auth-Type CHAP {
chap
}
Auth-Type MS-CHAP {
mschap
}
digest
unix
eap
}
preacct {
preprocess
acct_unique
suffix
files
}
accounting {
detail
unix
radutmp
sql
exec
attr_filter.accounting_response
}
session {
radutmp
sql
}
post-auth {
sql
exec
Post-Auth-Type REJECT {
attr_filter.access_reject
}
}
pre-proxy {
}
post-proxy {
eap
}
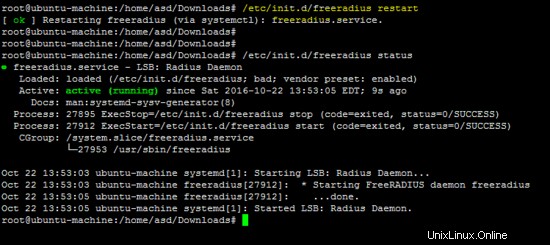
Utilizzare il comando seguente per riavviare il server freeradius e per verificare la configurazione.
/etc/init.d/freeradius restart
Configurazione del client Freeradius
Il comando seguente imposta il nome host e il segreto nel file "server" del client freeradius.
echo -e "localhost\ttesting123" >> /etc/radiusclient/servers
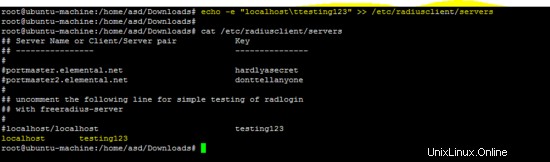
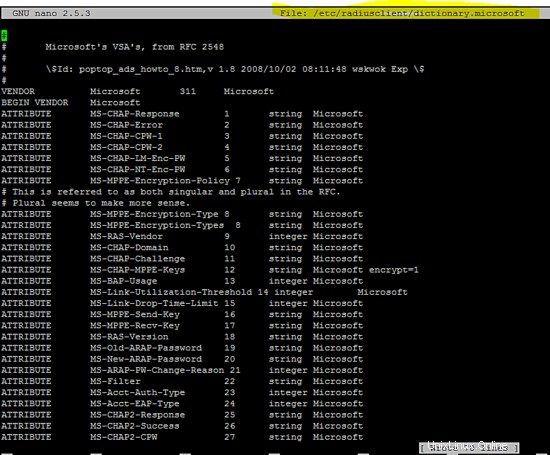
Crea il file di configurazione dictionary.microsoft per i client basati su Windows.
vi /etc/radiusclient/dictionary.microsoft
#
# Microsoft's VSA's, from RFC 2548
#
# \$Id: poptop_ads_howto_8.htm,v 1.8 2008/10/02 08:11:48 wskwok Exp \$
#
VENDOR Microsoft 311 Microsoft
BEGIN VENDOR Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-Response 1 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-Error 2 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-CPW-1 3 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-CPW-2 4 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-LM-Enc-PW 5 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-NT-Enc-PW 6 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-MPPE-Encryption-Policy 7 string Microsoft
# This is referred to as both singular and plural in the RFC.
# Plural seems to make more sense.
ATTRIBUTE MS-MPPE-Encryption-Type 8 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-MPPE-Encryption-Types 8 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-RAS-Vendor 9 integer Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-Domain 10 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-Challenge 11 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP-MPPE-Keys 12 string Microsoft encrypt=1
ATTRIBUTE MS-BAP-Usage 13 integer Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Link-Utilization-Threshold 14 integer Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Link-Drop-Time-Limit 15 integer Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-MPPE-Send-Key 16 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-MPPE-Recv-Key 17 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-RAS-Version 18 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Old-ARAP-Password 19 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-New-ARAP-Password 20 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-ARAP-PW-Change-Reason 21 integer Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Filter 22 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Acct-Auth-Type 23 integer Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Acct-EAP-Type 24 integer Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP2-Response 25 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP2-Success 26 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-CHAP2-CPW 27 string Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Primary-DNS-Server 28 ipaddr
ATTRIBUTE MS-Secondary-DNS-Server 29 ipaddr
ATTRIBUTE MS-Primary-NBNS-Server 30 ipaddr Microsoft
ATTRIBUTE MS-Secondary-NBNS-Server 31 ipaddr Microsoft
#ATTRIBUTE MS-ARAP-Challenge 33 string Microsoft
#
# Integer Translations
#
# MS-BAP-Usage Values
VALUE MS-BAP-Usage Not-Allowed 0
VALUE MS-BAP-Usage Allowed 1
VALUE MS-BAP-Usage Required 2
# MS-ARAP-Password-Change-Reason Values
VALUE MS-ARAP-PW-Change-Reason Just-Change-Password 1
VALUE MS-ARAP-PW-Change-Reason Expired-Password 2
VALUE MS-ARAP-PW-Change-Reason Admin-Requires-Password-Change 3
VALUE MS-ARAP-PW-Change-Reason Password-Too-Short 4
# MS-Acct-Auth-Type Values
VALUE MS-Acct-Auth-Type PAP 1
VALUE MS-Acct-Auth-Type CHAP 2
VALUE MS-Acct-Auth-Type MS-CHAP-1 3
VALUE MS-Acct-Auth-Type MS-CHAP-2 4
VALUE MS-Acct-Auth-Type EAP 5
# MS-Acct-EAP-Type Values
VALUE MS-Acct-EAP-Type MD5 4
VALUE MS-Acct-EAP-Type OTP 5
VALUE MS-Acct-EAP-Type Generic-Token-Card 6
VALUE MS-Acct-EAP-Type TLS 13
END-VENDOR Microsoft
vi /etc/radiusclient/dictionary.merit
#
# Experimental extensions, configuration only (for check-items)
# Names/numbers as per the MERIT extensions (if possible).
#
ATTRIBUTE NAS-Identifier 32 string
ATTRIBUTE Proxy-State 33 string
ATTRIBUTE Login-LAT-Service 34 string
ATTRIBUTE Login-LAT-Node 35 string
ATTRIBUTE Login-LAT-Group 36 string
ATTRIBUTE Framed-AppleTalk-Link 37 integer
ATTRIBUTE Framed-AppleTalk-Network 38 integer
ATTRIBUTE Framed-AppleTalk-Zone 39 string
ATTRIBUTE Acct-Input-Packets 47 integer
ATTRIBUTE Acct-Output-Packets 48 integer
# 8 is a MERIT extension.
VALUE Service-Type Authenticate-Only 8
Aggiungi le seguenti righe a /etc/radiusclient/dictionary file.
INCLUDE /etc/radiusclient/dictionary.merit
INCLUDE /etc/radiusclient/dictionary.microsoft
ATTRIBUTE Hourly-Traffic 1000 integer
ATTRIBUTE Daily-Traffic 1001 integer
ATTRIBUTE Monthly-Traffic 1002 integer
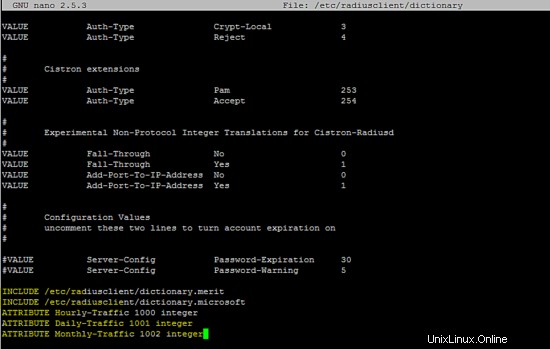
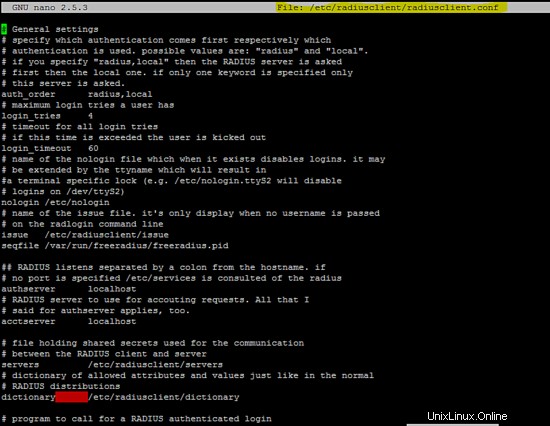
Quella seguente è la configurazione di esecuzione del client radius.
/etc/radiusclient/radiusclient.conf
# General settings
# specify which authentication comes first respectively which
# authentication is used. possible values are: "radius" and "local".
# if you specify "radius,local" then the RADIUS server is asked
# first then the local one. if only one keyword is specified only
# this server is asked.
auth_order radius,local
# maximum login tries a user has
login_tries 4
# timeout for all login tries
# if this time is exceeded the user is kicked out
login_timeout 60
# name of the nologin file which when it exists disables logins. it may
# be extended by the ttyname which will result in
#a terminal specific lock (e.g. /etc/nologin.ttyS2 will disable
# logins on /dev/ttyS2)
nologin /etc/nologin
# name of the issue file. it's only display when no username is passed
# on the radlogin command line
issue /etc/radiusclient/issue
seqfile /var/run/freeradius/freeradius.pid
## RADIUS listens separated by a colon from the hostname. if
# no port is specified /etc/services is consulted of the radius
authserver localhost
# RADIUS server to use for accouting requests. All that I
# said for authserver applies, too.
acctserver localhost
# file holding shared secrets used for the communication
# between the RADIUS client and server
servers /etc/radiusclient/servers
# dictionary of allowed attributes and values just like in the normal
# RADIUS distributions
dictionary /etc/radiusclient/dictionary
# program to call for a RADIUS authenticated login
login_radius /sbin/login.radius
# file which specifies mapping between ttyname and NAS-Port attribute
mapfile /etc/radiusclient/port-id-map
# default authentication realm to append to all usernames if no
# realm was explicitly specified by the user
default_realm
# time to wait for a reply from the RADIUS server
radius_timeout 10
# resend request this many times before trying the next server
radius_retries 3
# local address from which radius packets have to be sent
bindaddr *
# program to execute for local login
# it must support the -f flag for preauthenticated login
login_local /bin/login
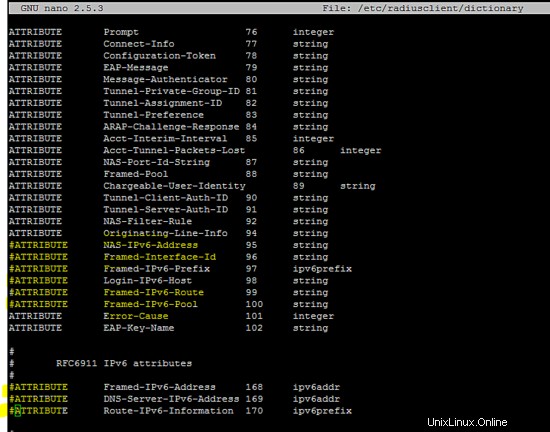
La configurazione seguente (relativa a IPv6) in /etc/radiusclient/dictionary file dovrebbe essere commentato per eseguire il client raggio.
ATTRIBUTE NAS-Filter-Rule 92 string
ATTRIBUTE Originating-Line-Info 94 string
ATTRIBUTE NAS-IPv6-Address 95 string
ATTRIBUTE Framed-Interface-Id 96 string
ATTRIBUTE Framed-IPv6-Prefix 97 ipv6prefix
ATTRIBUTE Login-IPv6-Host 98 string
ATTRIBUTE Framed-IPv6-Route 99 string
ATTRIBUTE Framed-IPv6-Pool 100 string
ATTRIBUTE Error-Cause 101 integer
ATTRIBUTE EAP-Key-Name 102 string
#
# RFC6911 IPv6 attributes
#
ATTRIBUTE Framed-IPv6-Address 168 ipv6addr
ATTRIBUTE DNS-Server-IPv6-Address 169 ipv6addr
ATTRIBUTE Route-IPv6-Information 170 ipv6prefix
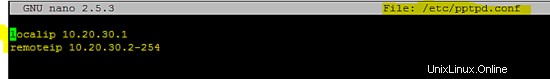
Configurazione del server Poptop
Aggiungi la seguente configurazione in /etc/pptpd.conf file.
localip 10.20.30.1
remoteip 10.20.30.2-254
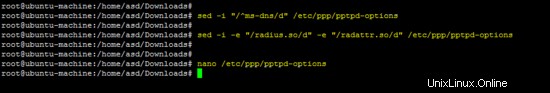
Esegui seguendo il comando sed su /etc/ppp/pptpd-options file.
sed -i "/^ms-dns/d" /etc/ppp/pptpd-options
sed -i -e "/radius.so/d" -e "/radattr.so/d" /etc/ppp/pptpd-options
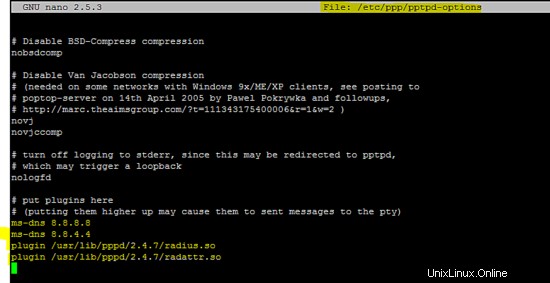
Aggiungi le seguenti righe in /etc/ppp/pptpd-options file.
ms-dns 8.8.8.8
ms-dns 8.8.4.4
plugin /usr/lib/pppd/2.4.7/radius.so
plugin /usr/lib/pppd/2.4.7/radattr.so
Riavvia il servizio pptpd per applicare le modifiche precedenti.
service pptpd restart
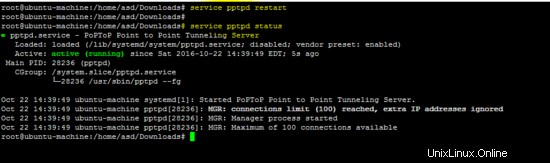
Configurazione di xl2tp
Includi le seguenti righe di configurazione in /etc/xl2tpd/xl2tpd.conf file come mostrato nella figura seguente.
[global]
ipsec saref = yes
[lns default]
ip range = 10.10.10.2-10.10.10.255
local ip = 10.10.10.1
refuse chap = yes
refuse pap = yes
require authentication = yes
ppp debug = yes
pppoptfile = /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd
length bit = yes
Configurazione di OpenSwan
Aggiungi la seguente impostazione del file segreto ipsec in /etc/ipsec.secrets .
192.168.15.4 %any 0.0.0.0: PSK "test"

La configurazione IPsec per il tunnel L2TP è inclusa in /etc/ipsec.conf file.
version 2.0
config setup
nat_traversal=yes
virtual_private=%v4:192.168.0.0/16,%v4:10.0.0.0/8,%v4:172.16.0.0/12,%v4:25.0.0.0/8,%v4:!10.254.253.0/24
protostack=netkey
#protostack=mast # used for SAref + MAST only
interfaces="%defaultroute"
oe=off
conn psk-l2tp
pfs=no
auto=add
rekey=no
# overlapip=yes # for SAref + MAST
# sareftrack=yes # for SAref + MAST
type=transport
left=192.168.15.4
leftprotoport=17/1701
right=%any
rightprotoport=17/%any
rightsubnet=vhost:%priv,%no
authby=secret
Configurazione del server PPP
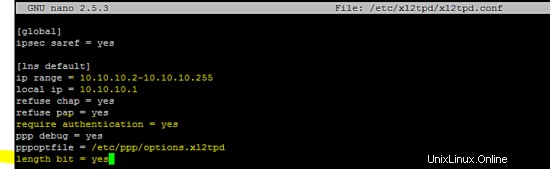
Aggiungi la seguente configurazione in /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd file.
ipcp-accept-local
ipcp-accept-remote
ms-dns 8.8.8.8
ms-dns 8.8.4.4
noccp
auth
crtscts
idle 1800
mtu 1200
mru 1200
nodefaultroute
debug
lock
proxyarp
connect-delay 5000
plugin /usr/lib/pppd/2.4.7/radius.so
plugin /usr/lib/pppd/2.4.7/radattr.so
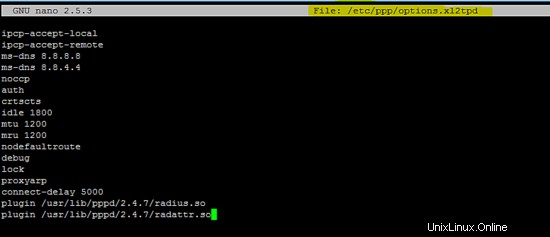
Dopo aver configurato correttamente tutti i pacchetti richiesti, ora riavvia tutti i servizi per testare la VPN L2TP.
Riavvio dei servizi IPsec e xl2tp.
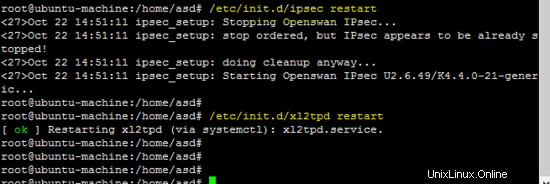
La figura seguente mostra che il server freeradius è in esecuzione in modalità demone, utile per identificare il funzionamento del server.
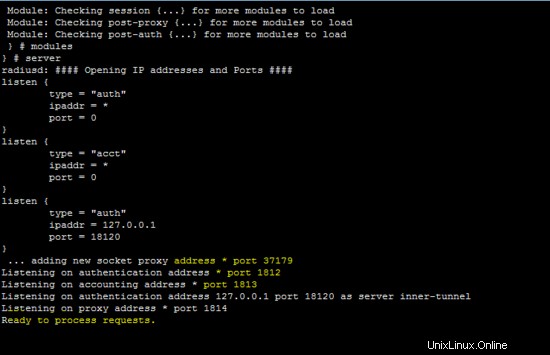
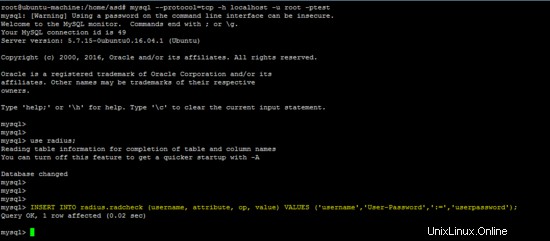
Inserisci un account utente nel database MySQL per testare la configurazione.
INSERT INTO radius.radcheck (username, attribute, op, value) VALUES ('username','User-Password',':=','userpassword');
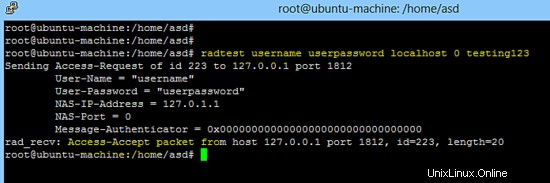
Il seguente comando verifica che il server Freeradius funzioni su localhost.
radtest username userpassword localhost 0 testing123
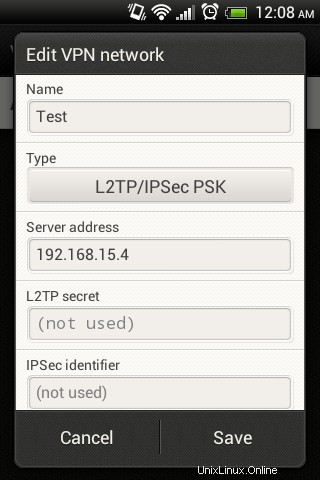
Configurazione del client Android L2TP
Vai a impostazioni ==> Altro ==> VPN ==>Aggiungi rete VPN sul telefono Android e crea il nuovo L2TP PSK VPN come mostrato di seguito.
Dopo aver creato la nuova VPN L2TP, fai clic su di essa e inserisci nome utente/password (configurata sul server freeradius).
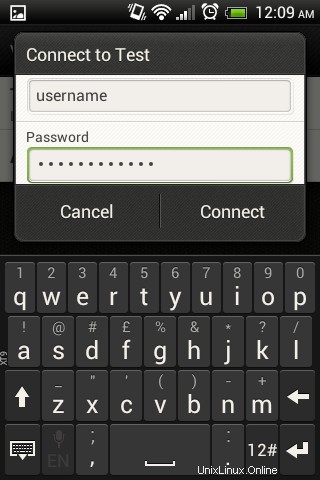
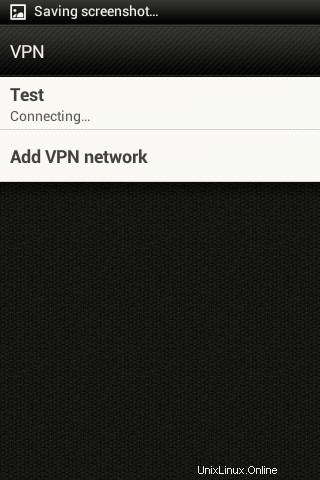
La figura seguente mostra che la VPN L2TP si sta connettendo.
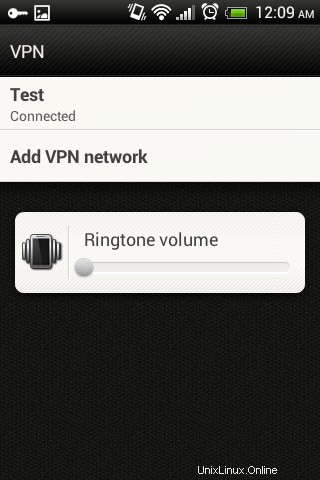
Le schermate seguenti mostrano che L2TP VPN è connesso correttamente utilizzando un client Android.
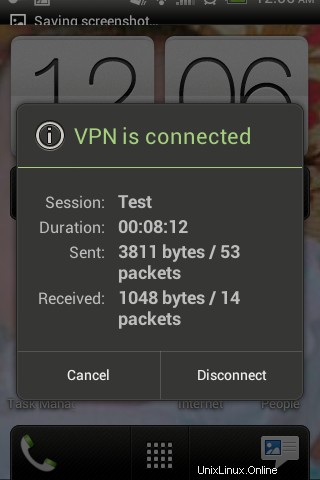
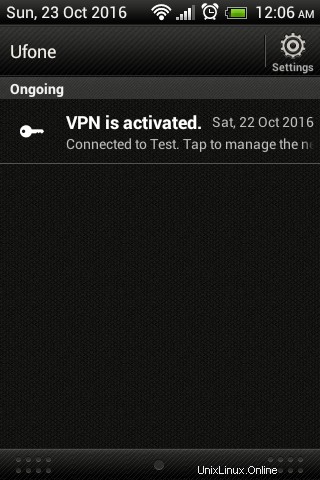
Stato VPN L2TP
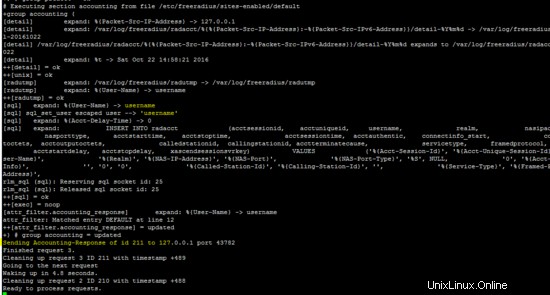
Freeradius mostra l'autenticazione riuscita del client Android L2TP.
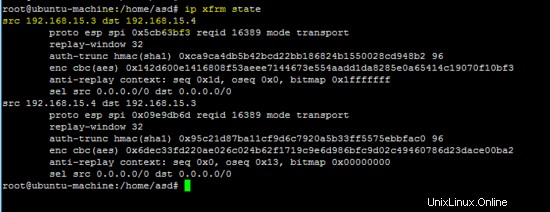
Il comando seguente mostra lo stato del tunnel IPsec
ip xfrm state
Registro di OpenSwan (/var/log/auth.log ) e registro xl2tp (/var/log/syslog ) mostra anche lo stato della VPN L2TP.
tail -f /var/log/auth.log
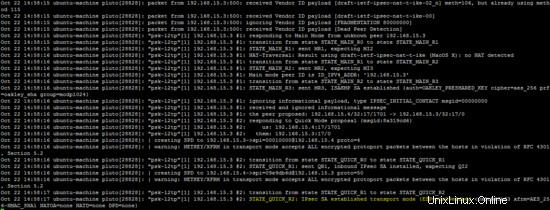
tail -f /var/log/syslog
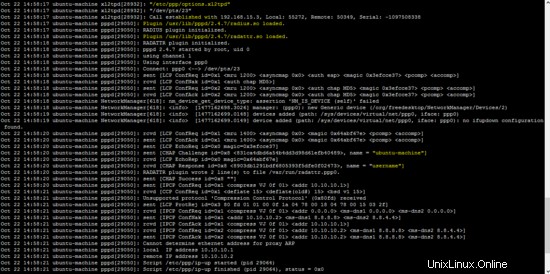
In questo tutorial, il protocollo di tunneling di livello 2 viene utilizzato con IPSec e Freeradius per fornire meccanismi di sicurezza e autenticazione. Un client basato su Android viene utilizzato per dimostrare il funzionamento di L2TP su IPsec.