Docker è una combinazione di prodotti platform as a service che utilizzano la virtualizzazione per fornire software in pacchetti chiamati container che possono comunicare tra loro attraverso canali ben definiti. Questo tutorial si concentra sull'installazione dell'ultima versione Docker su Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa.
In questo tutorial imparerai:
- Come installare Docker dal repository Ubuntu standard
- Come abilitare Docker per l'avvio dopo il riavvio del sistema
- Come consentire a un utente normale di amministrare Docker
 Docker su Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa
Docker su Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa Requisiti e convenzioni software utilizzati
| Categoria | Requisiti, convenzioni o versione del software utilizzata |
|---|---|
| Sistema | Installato Ubuntu 20.04 o aggiornato Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa |
| Software | Docker |
| Altro | Accesso privilegiato al tuo sistema Linux come root o tramite sudo comando. |
| Convenzioni | # – richiede che i comandi linux dati vengano eseguiti con i privilegi di root direttamente come utente root o usando sudo comando$ – richiede che i comandi linux dati vengano eseguiti come un normale utente non privilegiato |
Come installare Docker su Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa istruzioni passo passo
Installa Docker da un repository Ubuntu standard
- Usa
aptcomando per installaredocker.iopacchetto:sudo apt install docker.io
- Avvia la finestra mobile e abilita l'avvio dopo il riavvio del sistema:
$ sudo systemctl enable --now docker
- Facoltativamente, concedi a qualsiasi utente i privilegi di amministratore alla finestra mobile:
$ sudo usermod -aG docker SOMEUSERNAME
Dovrai disconnetterti e accedere per applicare le modifiche.
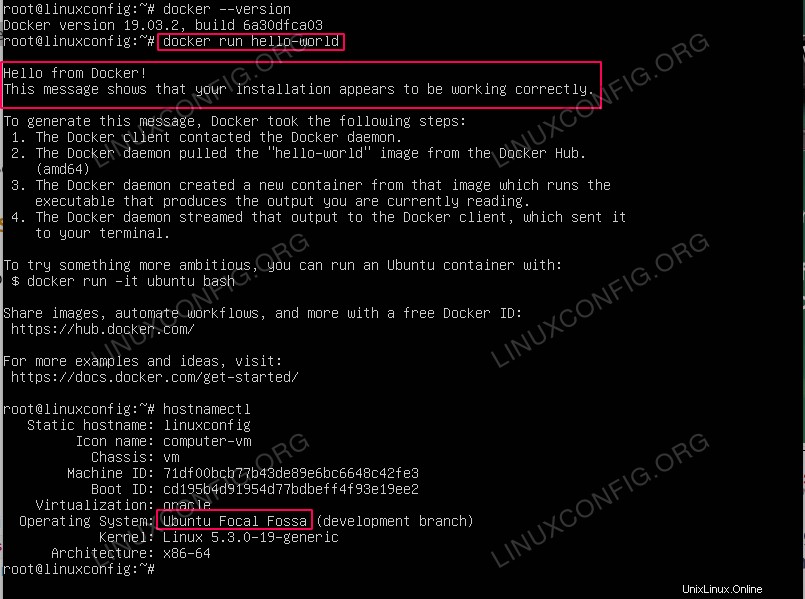
- Verifica versione docker:
$ docker --version
- Esegui il test Docker utilizzando
hello-worldcontainer:$ docker run hello-world Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. (amd64) 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminal. To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with: $ docker run -it ubuntu bash Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID: https://hub.docker.com/ For more examples and ideas, visit: https://docs.docker.com/get-started/