Come probabilmente saprai, Netstat (rete lavoro statistica istics) è uno strumento a riga di comando che può essere utilizzato per verificare la configurazione e l'attività della rete. Il comando netcat non è disponibile nell'installazione minima di RHEL 8, 7 e sono cloni come CentOS 8 e 7. Questo breve tutorial descrive come far funzionare il comando netstat nei sistemi CentOS 7, RHEL 7.
Una nota importante:
Come uno dei nostri lettori ha sottolineato nella sezione commenti qui sotto, molti dei vecchi comandi di rete Linux sono stati deprecati a favore delle loro controparti iproute2. Netstat in particolare è stato sostituito da “ss” comando disponibile per impostazione predefinita. Se usi ancora netstat per qualsiasi motivo, questo suggerimento potrebbe aiutarti.
comando netstat non trovato in CentOS 7/8 e RHEL 7/8
Per prima cosa vedremo come correggere questo errore nelle edizioni server CentOS 8 e RHEL 8.
Correzione dell'errore "comando netstat non trovato" in CentOS 8 e RHEL 8
Innanzitutto, dobbiamo trovare quale pacchetto fornisce 'netstat' comando utilizzando il seguente comando:
# dnf provides */netstat
Oppure,
# dnf whatprovides */netstat
Esempio di output dal mio server CentOS 8:
net-tools-2.0-0.51.20160912git.el8.x86_64 : Basic networking tools Repo : BaseOS Matched from: Filename : /usr/bin/netstat
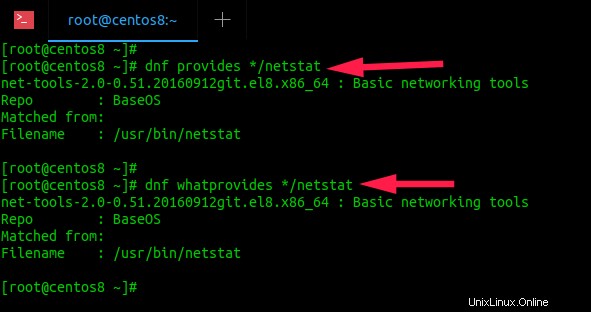
Come puoi vedere, il pacchetto "net-tools" fornisce il comando "netstat".
Quindi, installiamo il pacchetto net-tools come utente root usando il seguente comando come root utente:
# dnf install net-tools
Risultato di esempio:
CentOS-8 - AppStream 1.5 kB/s | 4.3 kB 00:02 CentOS-8 - Base 4.5 kB/s | 3.8 kB 00:00 CentOS-8 - Extras 1.7 kB/s | 1.5 kB 00:00 Dependencies resolved. ========================================================================================================================================================================== Package Architecture Version Repository Size ========================================================================================================================================================================== Installing: net-tools x86_64 2.0-0.51.20160912git.el8 BaseOS 323 k Transaction Summary ========================================================================================================================================================================== Install 1 Package Total download size: 323 k Installed size: 1.0 M Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: net-tools-2.0-0.51.20160912git.el8.x86_64.rpm 253 kB/s | 323 kB 00:01 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 170 kB/s | 323 kB 00:01 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : net-tools-2.0-0.51.20160912git.el8.x86_64 1/1 Running scriptlet: net-tools-2.0-0.51.20160912git.el8.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : net-tools-2.0-0.51.20160912git.el8.x86_64 1/1 Installed: net-tools-2.0-0.51.20160912git.el8.x86_64 Complete!
Ora puoi utilizzare il comando netstat sul tuo sistema CentOS 8.
Correzione dell'errore "comando netstat non trovato" in CentOS 7 e RHEL 7
In primo luogo, dovremmo scoprire quale pacchetto fornisce 'netstat' comando.
Per scoprirlo, esegui:
$ yum provides */netstat
Oppure,
$ yum whatprovides */netstat
Output di esempio:
yum provides */netstat Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirror.nbrc.ac.in * extras: mirror.nbrc.ac.in * updates: mirror.nbrc.ac.in net-tools-2.0-0.17.20131004git.el7.x86_64 : Basic networking tools Repo : base Matched from: Filename : /bin/netstat
Come vedi nell'output sopra, dobbiamo installare net-tools pacchetto per ottenere il comando netstat.
Quindi, installiamo il comando net-tools usando il seguente comando dal Terminale:
$ sudo yum install net-tools
Output di esempio:
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirror.nbrc.ac.in * extras: mirror.nbrc.ac.in * updates: mirror.nbrc.ac.in Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package net-tools.x86_64 0:2.0-0.17.20131004git.el7 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ======================================================================================================================================================================== Package Arch Version Repository Size ======================================================================================================================================================================== Installing: net-tools x86_64 2.0-0.17.20131004git.el7 base 304 k Transaction Summary ======================================================================================================================================================================== Install 1 Package Total download size: 304 k Installed size: 917 k Is this ok [y/d/N]: y Downloading packages: net-tools-2.0-0.17.20131004git.el7.x86_64.rpm | 304 kB 00:00:05 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Installing : net-tools-2.0-0.17.20131004git.el7.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : net-tools-2.0-0.17.20131004git.el7.x86_64 1/1 Installed: net-tools.x86_64 0:2.0-0.17.20131004git.el7 Complete!
Ecco fatto. Ora puoi usare il comando 'netstat'.
$ netstat
Output di esempio:
Active Internet connections (w/o servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 0 0 server.ostechnix.com:ssh sk:54534 ESTABLISHED Active UNIX domain sockets (w/o servers) Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 10304 /run/systemd/shutdownd unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 10242 @/org/freedesktop/systemd1/notify unix 5 [ ] DGRAM 6104 /run/systemd/journal/socket unix 13 [ ] DGRAM 6106 /dev/log unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 14013 /var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 24798 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17856 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17874 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 15064 [...] unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17878 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17832 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17841 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 14010 /var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 14710 /var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 11594 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 16500 /run/systemd/journal/stdout unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17809 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17836 unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 13906 unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 17845
Spero che questo aiuti.
Lettura consigliata:
- Come scoprire quale servizio è in ascolto su una determinata porta
- Come trovare le interfacce di rete disponibili su Linux