FileRun è un'applicazione di condivisione file gratuita, open source e self-hosted per Linux. È un'ottima alternativa a Google Drive e Dropbox. Ti consente di condividere e sincronizzare file, accedere tramite WebDAV e persino collegarti ad esso con l'app mobile Nextcloud. È scritto in PHP e utilizza MariaDB come backend del database. Ti consente di accedere ai tuoi file ovunque tramite un archivio cloud sicuro e offre anche il backup e la condivisione di foto, video, file e altro ancora.
In questo articolo spiegherò come installare FileRun con Apache e Let's Encrypt SSL su Debian 11.
Prerequisiti
- Un server che esegue Debian 11.
- Un nome di dominio valido puntato all'IP del tuo server.
- Sul server è configurata una password di root.
Installa il server LAMP
Innanzitutto, dovrai installare Apache, MariaDB, PHP e altri pacchetti sul tuo server. Puoi installarli tutti eseguendo il seguente comando:
apt-get install apache2 mariadb-server mariadb-client php libapache2-mod-php imagemagick ffmpeg php-imagick php-mysql php-fpm php-common php-gd php-json php-curl php-zip php-xml php-mbstring php-bz2 php-intl unzip -y
Una volta installati tutti i pacchetti, dovrai installare anche il caricatore IonCube sul tuo sistema.
Innanzitutto, scarica il caricatore IonCube con il seguente comando:
wget https://downloads.ioncube.com/loader_downloads/ioncube_loaders_lin_x86-64.tar.gz
Una volta completato il download, estrai il file scaricato con il seguente comando:
tar -xzf ioncube_loaders_lin_x86-64.tar.gz -C /usr/lib/php
Quindi, crea un file di configurazione di ioncube e definisci il percorso della sorgente di IonCube:
nano /etc/php/7.4/apache2/conf.d/00-ioncube.ini
Aggiungi la seguente riga:
zend_extension = /usr/lib/php/ioncube/ioncube_loader_lin_7.4.so
Salva e chiudi il file, quindi crea un file di configurazione PHP per FileRun:
nano /etc/php/7.4/apache2/conf.d/filerun.ini
Aggiungi le seguenti impostazioni:
expose_php = Off error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE display_errors = Off display_startup_errors = Off log_errors = On ignore_repeated_errors = Off allow_url_fopen = On allow_url_include = Off variables_order = "GPCS" allow_webdav_methods = On memory_limit = 128M max_execution_time = 300 output_buffering = Off output_handler = "" zlib.output_compression = Off zlib.output_handler = "" safe_mode = Off register_globals = Off magic_quotes_gpc = Off upload_max_filesize = 20M post_max_size = 20M enable_dl = Off disable_functions = "" disable_classes = "" session.save_handler = files session.use_cookies = 1 session.use_only_cookies = 1 session.auto_start = 0 session.cookie_lifetime = 0 session.cookie_httponly = 1 date.timezone = "UTC"
Salva e chiudi il file, quindi riavvia il servizio Apache per applicare le modifiche:
systemctl reload apache2
Configura il database MariaDB
Innanzitutto, dovrai proteggere l'installazione di MariaDB utilizzando il seguente comando:
mysql_secure_installation
Rispondi a tutte le domande come mostrato di seguito:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): PRESS ENTER Set root password? [Y/n] Y New password: Re-enter new password: Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
Quindi, accedi alla shell MariaDB con il seguente comando:
mysql -u root -p
Una volta effettuato l'accesso, crea un database e un utente con il seguente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE filerun;
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'filerun'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Quindi, concedi tutti i privilegi al database FileRun con il seguente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON filerun.* TO 'filerun'@'localhost';
Quindi, svuota i privilegi ed esci da MariaDB con il seguente comando:
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> EXIT;
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Scarica FileRun
Innanzitutto, scarica l'ultima versione di FileRun con il seguente comando:
wget -O FileRun.zip https://filerun.com/download-latest
Una volta scaricato FileRun, decomprimere il file scaricato utilizzando il seguente comando:
unzip FileRun.zip -d /var/www/html/filerun/
Quindi, imposta l'autorizzazione e la proprietà appropriate con il seguente comando:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/filerun
chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/filerun
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Configura Apache per FileRun
Successivamente, dovrai creare un file di configurazione dell'host virtuale Apache per FileRun. Puoi crearlo con il seguente comando:
nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/filerun.conf
Aggiungi le seguenti righe:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName filerun.example.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/filerun
<Directory "/var/www/html/filerun">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/filerun.error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/filerun.access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Salva e chiudi il file, quindi attiva l'host virtuale Apache e riscrivi il modulo con il seguente comando:
a2ensite filerun.conf
a2enmod rewrite
Quindi, riavvia il servizio Apache per applicare le modifiche:
systemctl restart apache2
Puoi anche controllare lo stato di Apache con il seguente comando:
systemctl status apache2
Dovresti vedere il seguente output:
? apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-01-29 15:14:56 UTC; 5s ago
Docs: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
Process: 22533 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/apachectl start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 22538 (apache2)
Tasks: 6 (limit: 2341)
Memory: 16.4M
CPU: 94ms
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
??22538 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??22539 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??22540 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??22541 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??22542 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??22543 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
Jan 29 15:14:56 debian11 systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
Una volta terminato, puoi procedere al passaggio successivo.
Accedi all'interfaccia utente Web di FileRun
Ora apri il tuo browser web e accedi all'interfaccia utente web di FileRun utilizzando l'URL http://filerun.example.com . Verrai reindirizzato alla seguente pagina:
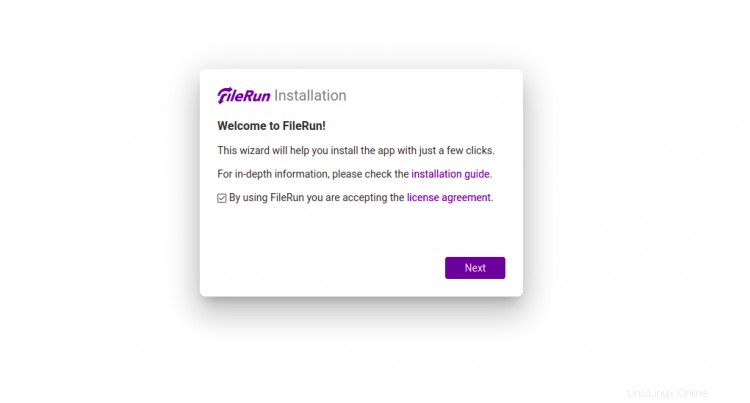
Fare clic su Avanti pulsante. dovresti vedere la pagina di controllo dei requisiti del server:
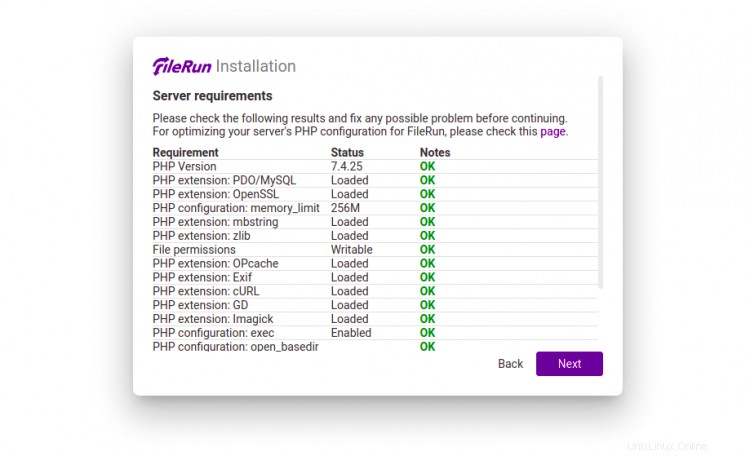
Fare clic su Avanti pulsante. Dovresti vedere la pagina di configurazione del database:

Fare clic su Avanti pulsante. Una volta terminata l'installazione, dovresti vedere la seguente pagina:

Fare clic su Avanti pulsante. Dovresti vedere la pagina di accesso di FileRun:

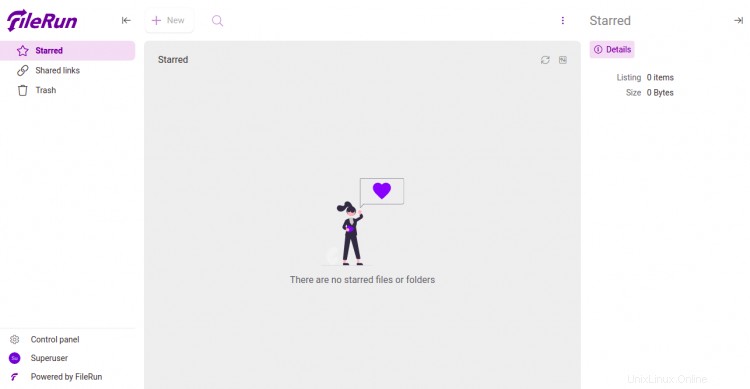
Fornisci il nome utente e la password dell'amministratore e fai clic su Accedi pulsante. Dovresti vedere la dashboard di FileRun nella pagina seguente:
FileRun sicuro con Let's Encrypt SSL
Si consiglia inoltre di proteggere il tuo sito Web con Let's Encrypt SSL. Innanzitutto, dovrai installare il client Certbot per installare e gestire SSL. Per impostazione predefinita, il pacchetto Certbot è incluso nel repository predefinito di Debian, quindi puoi installarlo con il seguente comando:
apt-get install python3-certbot-apache -y
Una volta installato Certbot, esegui il comando seguente per proteggere il tuo sito Web con Let's Encrypt SSL:
certbot --apache -d filerun.example.com
Ti verrà chiesto di fornire la tua email e di accettare i termini del servizio come mostrato di seguito:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator standalone, Installer None Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for filerun.example.com Enabled Apache rewrite module Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Created an SSL vhost at /etc/apache2/sites-available/filerun-le-ssl.conf Enabled Apache socache_shmcb module Enabled Apache ssl module Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/apache2/sites-available/filerun-le-ssl.conf Enabling available site: /etc/apache2/sites-available/filerun-le-ssl.conf Next, select whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS as shown below:
Scegli se reindirizzare o meno il traffico HTTP su HTTPS, rimuovendo l'accesso HTTP.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Digita 2 e premi Invio per installare Let's Encrypt SSL per il tuo sito web:
Enabled Apache rewrite module Redirecting vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/filerun.conf to ssl vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-available/filerun-le-ssl.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://filerun.example.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=filerun.example.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/filerun.example.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/filerun.example.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2022-4-29. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Conclusione
Congratulazioni! hai installato correttamente FileRun con Apache e Let's Encrypt SSL su Debian 11. Ora puoi utilizzare FileRun per archiviare file, musica, foto e condividerli con amici e familiari.