LAMP è l'abbreviazione di L inux, A pache, M ySQL, P HP. Questo tutorial mostra come installare un server Web Apache su un server Debian Stretch (9) con supporto per PHP 7 (mod_php) e MariaDB. MariaDB è un fork del noto server di database MySQL, fornisce un set di funzionalità compatibili con MySQL ed è un po' più veloce secondo i benchmark che ho trovato su Internet. MariaDB funzionerà con tutte le applicazioni che richiedono MySQL come Wordpress, Joomla ecc.
Una configurazione LAMP è una base perfetta per sistemi CMS come Joomla, Wordpress o Drupal.
1 Nota preliminare
In questo tutorial, utilizzo il nome host server1.example.com con l'indirizzo IP 192.168.1.100. Queste impostazioni potrebbero differire per te, quindi devi sostituirle dove appropriato.
2 Installazione di MariaDB come sostituto di MySQL
Innanzitutto, installiamo MariaDB in questo modo:
apt-get -y install mariadb-server mariadb-client
Successivamente, metteremo al sicuro MariaDB con mysql_secure_installation comando. Esegui il comando seguente e segui la procedura guidata.
mysql_secure_installation
L'input consigliato è mostrato in rosso.
mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): <-- Hit return
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] <-- y
New password: <-- Enter the new password for the MariaDB root user
Re-enter new password: <-- Enter the password again
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] <-- y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] <-- y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] <-- y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] <-- y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
La configurazione di MariaDB è ora protetta.
3 Installazione del server web Apache
Apache è disponibile come pacchetto Debian, quindi possiamo installarlo in questo modo:
apt-get -y install apache2
Ora indirizza il tuo browser a http://192.168.1.100 e dovresti vedere la pagina segnaposto Apache2 (Funziona!):
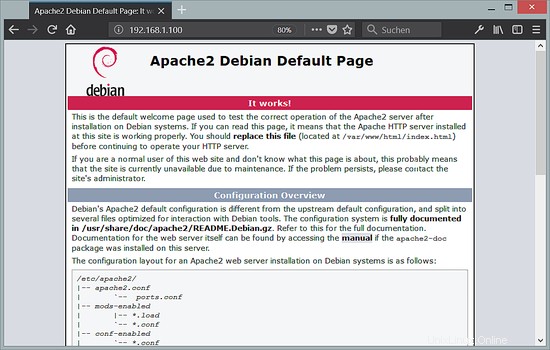
La radice del documento predefinita di Apache è /var/www su Debian e il file di configurazione è /etc/apache2/apache2.conf. Ulteriori configurazioni sono archiviate in sottodirectory della directory /etc/apache2 come /etc/apache2/mods-enabled (per moduli Apache), /etc/apache2/sites-enabled (per host virtuali) e /etc/apache2/conf -abilitato.
4 Installazione di PHP 7.1
Possiamo installare PHP e il modulo Apache PHP come segue:
apt-get -y install php7.0 libapache2-mod-php7.0
Dobbiamo riavviare Apache in seguito:
service apache2 restart
5 Test di PHP / Ottenere dettagli sulla tua installazione di PHP
La radice del documento del sito Web predefinito è /var/www/html. Ora creeremo un piccolo file PHP (info.php) in quella directory e lo chiameremo in un browser. Il file mostrerà molti dettagli utili sulla nostra installazione di PHP, come la versione di PHP installata.
nano /var/www/html/info.php
<?php
phpinfo();
Ora chiamiamo quel file in un browser (es. http://192.168.1.100/info.php):
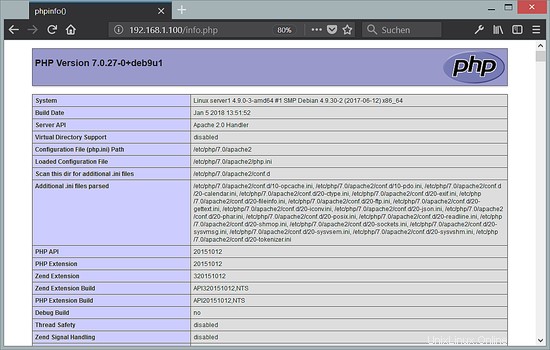
Come vedi, PHP 7.0 funziona e funziona tramite il gestore Apache 2.0, come mostrato nella riga dell'API del server. Se scorri più in basso, vedrai tutti i moduli che sono già abilitati in PHP5. MySQL / MariaDB non è elencato lì, il che significa che non abbiamo ancora il supporto per MySQL in PHP5.
6 Ottenere il supporto per MySQL e MariaDB in PHP
Per ottenere il supporto MySQL in PHP, installeremo il pacchetto php7.0-mysql. È una buona idea installare alcuni altri moduli PHP e potresti averne bisogno per le tue applicazioni. Puoi cercare i moduli PHP 7 disponibili in questo modo:
apt-cache search php7.0
Scegli quelli che ti servono e installali in questo modo:
apt-get -y install php7.0-mysql php7.0-curl php7.0-gd php7.0-intl php-pear php-imagick php7.0-imap php7.0-mcrypt php-memcache php7.0-pspell php7.0-recode php7.0-sqlite3 php7.0-tidy php7.0-xmlrpc php7.0-xsl
Ora riavvia Apache:
service apache2 restart
7 PHP Cache per migliorare la velocità di PHP
Per velocizzare PHP, dovrebbe essere installato un Opcache. Controlla se il modulo PHP Opcache è stato installato e abilitato correttamente. Esegui questo comando:
php --version
L'output deve contenere la riga che ho segnato in rosso.
PHP 7.0.27-0+deb9u1 (cli) (built: Jan 5 2018 13:51:52) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) 1997-2017 The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.0.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2017 Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v7.0.27-0+deb9u1, Copyright (c) 1999-2017, by Zend Technologies
Se non vedi il modulo Opcache nel risultato, installalo con questo comando:
apt-get -y install php7.0-opcache
C'è un'altra cache che potrebbe essere utile, il suo nome è APCu. APCu è un cacher di codice operativo PHP gratuito per la memorizzazione nella cache e l'ottimizzazione del codice intermedio PHP.
L'APCu può essere installato come segue:
apt-get -y install php-apcu
Ora riavvia Apache:
service apache2 restart
Ora ricarica http://192.168.1.100/info.php nel tuo browser e scorri di nuovo verso il basso fino alla sezione dei moduli. Ora dovresti trovare molti nuovi moduli lì, incluso il modulo MySQL che viene utilizzato come driver MariaDB:
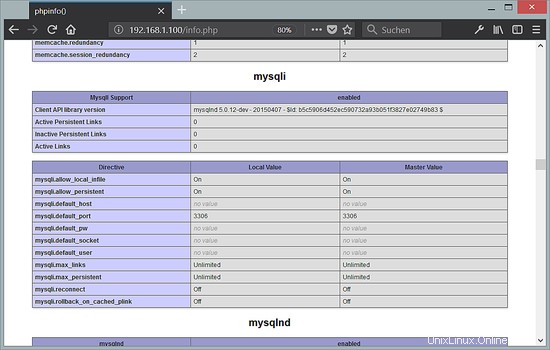
8 phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin è un'interfaccia web attraverso la quale puoi gestire i tuoi database MySQL e MariaDB. È una buona idea installarlo:
apt-get -y install phpmyadmin
Vedrai le seguenti domande:
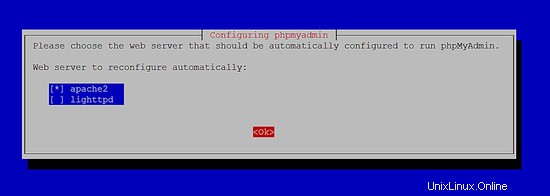
Web server to reconfigure automatically: <-- apache2
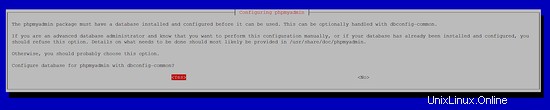
Configure database for phpmyadmin with dbconfig-common?<-- Yes
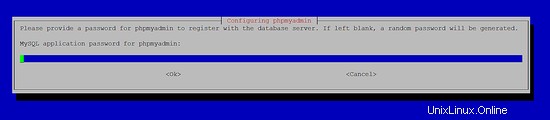
MySQL application password for phpmyadmin: <-- Press enter, apt will create a random password automatically.
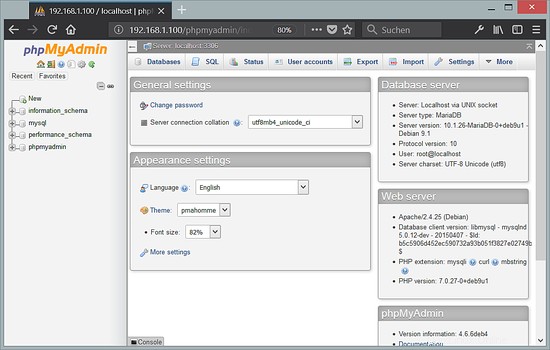
Successivamente, puoi accedere a phpMyAdmin da http://192.168.1.100/phpmyadmin/:
9 Abilita l'accesso root MySQL per phpMyAdmin
Sebbene tu possa accedere come utente root a MariaDB sulla shell, il login root non funzionerà in phpMyAdmin. Per consentire anche all'utente root di utilizzare phpMyAdmin, esegui il seguente comando sulla shell:
echo "UPDATE mysql.user SET plugin = 'mysql_native_password' WHERE user = 'root' AND plugin = 'unix_socket';FLUSH PRIVILEGES;" | mysql -u root -p
10 link
- Apache:http://httpd.apache.org/
- PHP:http://www.php.net/
- MySQL:http://www.mysql.com/
- Debian:http://www.debian.org/
- phpMyAdmin:http://www.phpmyadmin.net/